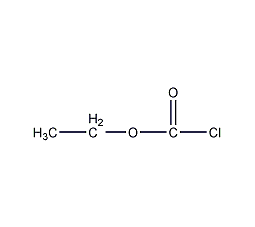
Structural formula
| Business number | 05KT |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H5CLO2 |
| Molecular weight | 108.53 |
| label |
Ethyl chloroalkanoate, Ethyl chloroformate, Ethyl chloroformate, Ethyl chlorocarbonate, Carbonchloridic acid ethyl ester, Cathyl chloride, Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:541-41-3
MDL number:MFCD00000644
EINECS number:208-778-5
RTECS number:LQ6125000
BRN number:385653
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless transparent liquid with pungent odor. [11]
2. Melting point (℃): -80.6[12]
3. Boiling point (℃): 95[13]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.14[14]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 3.74[15]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 2.98 (25℃)[16]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1280[17]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 235[18]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.5[19]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.63 [20]
11. Flash point (℃): 16 (CC) [21]
12. Ignition temperature (℃) ): 500[22]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 27.5[23]
14. Explosion lower limit (%): 3.2[24]
15. Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in most organic solvents such as benzene, chloroform, and ether. [25]
16. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5:22.215
17. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 7.470×109
18. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 50.720
19. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ· mol-1): -505.2
20. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 198.6
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 270 mg/kg, no detailed description except lethal dose; Rat inhalation LC50: 840 mg/m3/1H, changes in lungs, chest or respiratory-pulmonary, Total weight nutritional metabolism – reduced weight loss or weight gain; mouse inhalation LCLo: 2260 mg/m3/10M, no details other than lethal dose; mouse intraperitoneal LDLo: 15 mg/kg, no details other than lethal dose ; Rabbit skin LD50: 7120 mg/kg, no detailed description except the lethal dose;
2. Poisoning by inhalation, ingestion or skin absorption manifests as irritation to the eyes and upper respiratory tract. Pulmonary edema may occur at high concentrations.
3. Acute toxicity[26]
LD50: 270mg/kg (rat Oral); 7120mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 840mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 1h)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data yet
2. Biodegradability[27] Good Oxobiodegradation (h): 672~2688
3. Non-biodegradability[28]
The half-life of photooxidation in air (h): 44.5~445
The half-life of primary hydrolysis (h): 0.55
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 22.57
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 92.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 214.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 28.4
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.94
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.5
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 52.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It is flammable, toxic and corrosive. It will easily cause combustion and release toxic gases when exposed to open flames or high heat. Can be gradually decomposed by water.
2. It can be slowly hydrolyzed by water into carbon dioxide and hydrochloric acid. If stored at low temperature, it will decompose into carbon dioxide and ethyl chloride if the temperature is too high. This reagent is flammable, very toxic if inhaled or absorbed through the skin, has a pungent odor, and can produce tear-inducing effects.
3. Stability[29] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[30] Acids, strong bases, water, alcohols, amines
5. Conditions to avoid contact [31] Humid air
6. Polymerization hazard[32] No polymerization
7. Decomposition products [33] Hydrogen chloride, phosgene
Storage method
Storage Precautions[34] Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated special warehouse, and implement “two people to send and receive, and two people to keep” “system. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. They should be stored separately from acids, alkalis, alcohols, amines, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Originated from the reaction of ethanol and phosgene. The esterification reaction between phosgene and absolute ethanol produces ethyl chloroformate, which is then refined through impurity removal, dehydration, fractionation and other refining processes to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
1. Used in the photography industry as solvents and organic synthesis intermediates.
2. Acidification of sterol hydroxyl groups, alkylation of acid imines, ethoxycarbonylation of pyrrole rings and carboxylic acids, and preparation of carbamates and mixed acid anhydrides, etc.
3. Used to prepare ethyl urethane, diethyl formate, etc., and also used in medicine, pesticides, and flotation agents.
4. Ethyl chloroformate can realize a variety of nucleophiles such as carboxylic acid, ester, acetonitrile, dithiane, ketone, enamine, imine, sulfone, copper reagent, tin reagent, Grignard reagent Ethoxycarbonylation reaction of reagents, furans and alkynes; ethyl chloroformate can also realize the acylation reaction of alcohols, carbonyl groups, amines and cycloethylimines, as well as the cleavage reaction of tertiary amines.
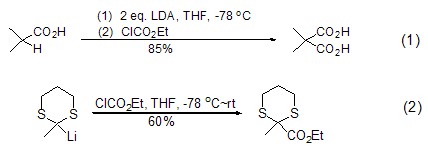
Ethyl chloroformate can effectively react with compounds containing active methylene groups to achieve ethoxycarbonylation. Usually alkyl and aryl carboxylic acids can be treated with the non-nucleophilic base lithium diisopropylamide LDA to activate α-H, and then react with ethyl chloroformate to obtain malonic acid. Monoesterification product (formula 1)[1]. α-lithiated nitrile, carboxylic aldehyde and 1,3-dithiane can directly interact with ethyl chloroformate to achieve ethoxycarbonylation reaction (Formula 2)[2].
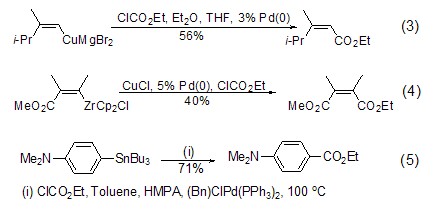
Except those containing active methylene In addition to compounds, vinyl anions can also react effectively with ethyl chloroformate. For example, vinyl copper reacts with ethyl chloroformate under the catalysis of Pd(0) to obtain α,β-Reaction of unsaturated esters (Formula 3)[3], for another example, vinyl zirconium reacts with ethyl chloroformate under the catalysis of CuCl/Pd(0) to obtain bifunctional olefins ( Formula 4)[4]. And aryl, vinyl and heterocyclic tin reagents can also be catalyzed by metal palladium complexes to obtain ortho-unsaturated ethyl ester products (formula 5)[5] in high yields.
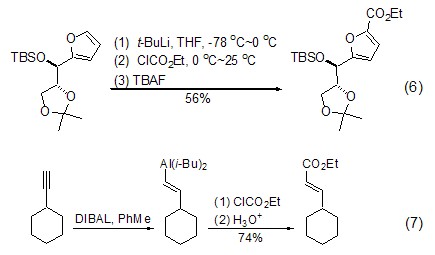
In addition, Grignard reagents, alkanes Lithium reagents and organoaluminum reagents can also activate the sp2-carbon of the substrate, thereby causing an ethoxyesterification reaction with ethyl chloroformate (Formula 6, Formula 7) [6,7].
Ethyl chloroformate can also realize the acylation reaction of functional groups containing O, N and S, such as cyclohexanone. The lithiated enol structure is obtained by treatment with lithium reagent, and then reacts with ethyl chloroformate to achieve the ethyl ester reaction on O (formula 8)[8].

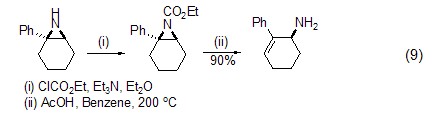
Ethyleneimine can interact directly with ethyl chloroformate in an alkaline environment , the ethyl esterification reaction on N occurs (formula 9)[9].
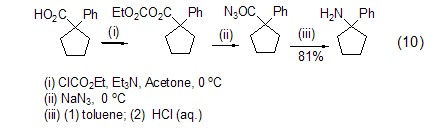
Ethyl chloroformate and carboxylic acid can directly react under alkaline conditions to form a mixed acid anhydride, which can then achieve other reactions, such as the preparation of acyl azide compounds (formula 10)[10].
5. Used in organic synthesis and as solvent.[35]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

