1. Crude benzene products and their uses
Crude benzene is a yellow transparent liquid and a mixture of various organic compounds. Crude benzene itself has little use, but products such as pure benzene (C6H6), toluene (C6H5CH3) and xylene {C6H4(CH3)2 can be obtained by refining and processing crude benzene. Pure benzene is used in man-made fibers, plastics, drugs and fuels, toluene is used in the manufacture of explosives and synthetic fibers, and xylene is used as a solvent in rubber and paint and as an additive in aviation and internal combustion engine fuels. In short, crude benzene is a very valuable basic chemical raw material.
2. Composition, properties and quality of crude benzene
2.1 Composition of crude benzene
The composition of crude benzene fluctuates greatly, mainly depending on the composition of the coking coal blend and the degree of pyrolysis of the coking products in the carbonization chamber (and the carbonization temperature of the coke oven). The average content of the main components of crude benzene is as follows:
Benzene 55-80%: Toluene 11-22%: Xylene 2-6%: Unsaturated compounds (such as cyclopentadiene (C5H6) styrene (C6H5CHCH2), etc. 7-12%: Sulfide (such as carbon disulfide) (CS2) Thiophene (C4H4S), etc. 0.3-1.8%.
2.2 Properties of crude benzene
Crude benzene is lighter than water, slightly soluble in water, and easily separated from water. When stored for a long time, the resinous substances formed by the oxidation and polymerization of unsaturated compounds are dissolved in crude benzene, which can cause the color of crude benzene to dark brown (or light red). Crude benzene is flammable with a flash point of 12°C. When the volume concentration of crude benzene vapor in the air is 1.4%-7.5%, it can form an explosive mixture. If crude benzene catches fire, foam or steam should be used to extinguish the fire. Crude benzene can easily generate static electricity when flowing in pipelines. To prevent the risk of static sparks, equipment and pipelines for crude benzene production, product transportation and storage should be installed with reliable grounding conductive devices.
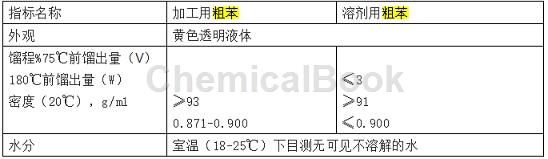
2.3 Quality and indicators of crude benzene
The main components of crude benzene are all distilled before 180°C, and the outflow after 180°C is calculated as 100%. Therefore, the distillation amount before 180°C is used as one of the indicators to identify the quality of crude benzene. . The amount of crude benzene distilled before 180°C depends on the process flow and operating system of the crude benzene section. The more distillation volume before 180℃, the better the quality of crude benzene. Generally, the distillation volume of crude benzene before 180℃ is required to be 91%-93%. The quality index of crude benzene is as follows.
3. Estimation of crude benzene production
3.1 Crude benzene yield
The crude benzene yield is related to the quality of the charging coal, coking temperature and the visible temperature of the coke oven top. It increases with the increase of the volatile content of the charging coal and decreases with the increase of the coking temperature and the visible temperature of the furnace top.
The yield of crude benzene can be calculated according to the following empirical formula: (1) y=a+bv
In the formula: y——crude benzene yield (for coal)%
V——combustible volatile matter of coking coal, %
a, b——constants
Constants a and b vary depending on the properties of the furnace coal and the main process conditions of each plant. Under certain conditions a and b are constant values. Taking a coking plant as an example: a=-0.64, b=0.065 (scope of application: v=27.96—30.37%, y=0.0988—1.37%))
2. y=-1.6+0.144v-0.0016(v)2
The symbols in the formula have the same meaning as above (v is between 20-30%).
The crude benzene yield is generally 0.75%-1.1% of the coking dry basis blended coal, that is, when coking with coking washed coal, 7.5-11 kg of crude benzene can be obtained without using a single meal of dry coal. Coke oven gas generally contains crude benzene at 25-40g/m3.
3.2 Estimation of crude benzene production
(1) Basic data (example)
Coal consumption in coke oven (average) 50t/h (dry basis)
Net gas yield 320-330Nm3/t dry coal, value 325 m3/t
The benzene content of the gas before the benzene washing tower is 28g/m3
The benzene content of the gas after benzene washing tower is 3g/m3
Crude benzene output (for dry coal) 0.82%
(2) Crude benzene output
a. Estimated based on the benzene content in the gas (the benzene content of the gas in actual production can be obtained by laboratory analysis):
50*325*(28-3)/1000=406.25kg
That is, it can produce about 10 tons of crude benzene every day.
b. Estimated based on crude benzene yield:
50*0.0082*1000=410kg/h
That is, about 10 tons of crude benzene can be produced every day.
4. Indicators of consumption of washing oil, steam and coke oven gas in crude benzene production
(1) Washing oil <100kg/t crude benzene (some domestic coking plants <70kg/t crude benzene);
(2) Steam 10-1.5t/t crude benzene;
(3) Coke oven gas 450-550m3/t crude benzene.
5. The basic principle of washing oil absorbing crude benzene
Using washing oil to absorb crude benzene in coke oven gas is a physical absorption process, obeying Henry’s law and Dalton’s law of gas partial pressure. When the partial pressure of crude benzene vapor in the gas is greater than the vapor pressure of crude benzene on the washing oil surface, the crude benzene in the gas is absorbed by the washing oil.
6. Method for recovering crude benzene from coke oven gas
(1) Absorption of crude benzene part
a. Washing oil absorption method (adopted by our company): Use washing oil to absorb the crude benzene in the coke oven gas in a special washing tower, and send the washing oil (called rich oil) that has absorbed the crude benzene to the dewatering station. In the benzene tower distillation unit, crude benzene is extracted, and the washed oil after benzene removal (called lean oil) is cooled and sent back (circulated) to the washing tower to absorb the crude benzene.
b. Adsorption method (if activated carbon is used to adsorb crude benzene in coal gas, it can be used as one of the analytical methods for benzene-containing gas)
c. Low temperature pressurization method
(2) Distillation and benzene removal part
The washing oil that has absorbed the crude benzene in the gas is called rich oil. According to the occurrence of oil-rich heating, it is divided into:
a. The preheater heats the rich oil (��Water vapor as heat source) debenzene removal method.
b. Debenzene removal method by heating rich oil in a tube furnace (using coke oven gas as the main heat source).
7. The principle of distilling crude benzene from rich oil
The reason for steaming crude benzene from rich oil is based on the difference in boiling point 2 between the wash oil and crude benzene. Although the boiling point of crude benzene is less than 180°C, its liquid mixture does not have a constant boiling point, and the wash oil is this mixture. The main component in the mixture, so the boiling point of the mixture is between the boiling point of crude benzene and wash oil (230-300°C), and is close to the boiling point of the wash oil, so a steam distillation method that lowers the distillation temperature is used.
8. Process introduction and flow chart of crude benzene section
8.1 Process Introduction
The gas from the ammonium sulfate section enters the final cooling tower, where it is cooled to 25-28°C, then enters the benzene washing tower from the bottom of the tower, where it contacts the wash oil (lean oil) coming down from the top of the tower in countercurrent Finally, the benzene hydrocarbons in the gas are absorbed by the lean oil in the wash oil, and part of the gas from the top of the tower is returned to the coke oven for heating. The rest is sent to users such as gas cabinets.
After absorbing the lean oil of benzene hydrocarbons and turning it into rich oil, a small rich oil pump is fed into the bottom of the benzene washing tower and sent to the rich oil tank. It is pumped from Dafu Oil to the benzene steaming section for processing. The hot lean oil after benzene removal passes through the first stage lean oil heat exchanger and enters the hot lean oil tank at the bottom of the benzene removal tower. It is then extracted from the tank with a lean oil pump and passes through the second stage lean oil heat exchanger. , the second stage lean oil cooler is cooled and sent to the top of the benzene washing tower for spraying.
The rich oil from the benzene washing tower is pumped into the oil-gas heat exchanger to exchange heat with the benzene steam at the top of the benzene removal tower, and then enters the second and first stage lean oil heat exchangers to exchange heat with the hot lean oil from the benzene removal tower. Then it enters the convection section and radiant section of the tube furnace to heat the rich oil to 180±5℃ and then enters the debenzene tower for distillation. About 1-2% of the rich oil enters the regenerator, is steamed with superheated steam, and steams out from the top of the regenerator. The gas enters the benzene removal tower, and the residue discharged from the lower part flows into the residue tank.
The benzene vapor from the benzene removal tower enters the condensation cooler, first exchanges with the rich oil heat exchanger and then enters the oil-water separator. The crude benzene flows into the reflux column, part of which is sent to the top of the benzene removal tower for reflux by a reflux pump, and the rest flows into the crude benzene The intermediate tank is regularly sent to the benzene library by product pump.
The oil-water separator separates water and flows into the control separator to further separate oil and water. The crude benzene flows into the intermediate tank, and the water goes to the vent tank for treatment.
9. Overview of the main production process equipment in the crude benzene section
(1) Two gas cross-tube final coolers (F=3100m2) (one on and one on standby), designed to process 33740m3/h of coke oven gas, with circulating condensate spraying devices at the top and middle to mechanically Flushing and adsorbing naphthalene and tar dust attached to the inner cross tube wall of the final cooler. The top is the gas inlet and the bottom is the gas outlet. Its structure is basically the same as that of the gas horizontal tube primary cooler.
(2) Two final cooling spray liquid pumps (one on and one on standby), with a flow rate of 20m3/h, a lift of 50m, and a matching motor of 7.5KW.
(3) 1 benzene washing tower, Dn3.6m; H=32m. The function of the benzene washing tower is to fully contact the circulating washing oil (lean oil) and gas in the tower, thus achieving the benzene washing effect. The benzene washing tower is an upright circular light porcelain packed tower made of welded steel plates.
(4) 1 debenzene removal tower, Dn1.6m, 3 trays, below the 15th tray is the stripping section, and above the 15th tray is the rectification section. A bubble cap is installed on each tray. There are many slits on the bubble cap for steam to pass from bottom to top. There is also an overflow pipe on the tray for liquid to flow from top to bottom. In this way, the gas and liquid two-phase mass transfer is carried out. The heat partially vaporizes the low-boiling-point fractions in the liquid, while the high-boiling-point fractions in the steam are partially condensed. After repeated partial vaporization and condensation through multiple layers of trays, the high-boiling point wash oil is enriched in the tray liquid. (This is called hot lean oil), the benzene vapor of low boiling point components is enriched in the steam at the top of the tower, so that the crude benzene in the rich oil is steamed out. The benzene removal tower is made of welded stainless steel plates and has a rich oil processing capacity of 45-55m3/h.
(5) One tubular heating furnace with a total heat load of 2.97 MW/h. It is an upright cylindrical tubular furnace with a convection section and a heat radiation section. Its function is to heat rich oil and saturated water vapor. The superheated steam is used to remove benzene from rich oil and used as direct heating steam.
(6) 3 thermal lean oil pumps and rich oil pumps (2 open and 1 standby), rated flow rate 50m3/h; head H=125m, equipped with motor power 37KW.
(7) 2 crude benzene reflux pumps (1 open and 1 standby), rated flow 6.25m3/h, lift = 36m, supporting motor power 3KW. Its function is to send crude benzene to the top of the benzene removal tower for reflux. To control the temperature at the top of the tower to produce qualified products.
(8) Wash oil regenerator. The function of the regenerator is to remove high-boiling polymer components in the wash oil to improve the quality of the circulating wash oil. At the same time, it also provides direct heating steam to the benzene removal tower. The regenerator is used An upright cylinder made of welded steel plates with a tapered bottom. The principle of circulating wash oil (rich oil) regeneration is that due to the cyclic heating of the wash oil, the high boiling point components in the wash oil polymerize to generate residues. Through the wash oil regenerator, steam heat and steam blowing are used to evaporate the low boiling point components of the rich oil. out, and discharge the circulating washing oil residue.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

