Background and overview[1][2]
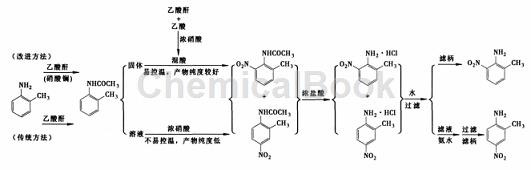
2-Methyl-6-nitroaniline, also known as 2-amino-3-nitrotoluene, is an important fine chemical intermediate and dye intermediate, widely used in organic synthesis, printing and dyeing, rubber It is an important raw material in industries such as pharmaceuticals, plastics and paints. It has a suitable melting point and can also be used as a component of mixed explosives. The traditional method uses a one-pot cooking method to synthesize 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline, that is, after the acetylation reaction of o-toluidine, the nitration reaction is directly performed in the same reactor, and then the nitration product is separated, and then deacetylated with hydrochloric acid to obtain 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline. – A method of separating the hydrochloride mixture of methyl-6-nitroaniline and 2-methyl-4-nitroaniline by diluting the hydrochloride with water.
The one-pot cooking method involves both nitrification exotherm and acid preparation exotherm. The temperature is difficult to control, prone to danger, and requires extremely high equipment and operation requirements. It is difficult to apply to large-scale industrial production, and 2-methyl- 6-Nitroaniline is less pure. The highest yield of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline was 59.7% with a purity of only 97%.
In view of the shortcomings of the traditional one-pot cooking method, some studies have carried out the acetylation reaction and the nitration reaction step by step, that is, first prepare the acetylation product, and then add it to the pre-prepared nitration reagent to obtain the acetylation nitration product mixture. , hydrolyze with hydrochloric acid to obtain a mixture of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline and 2-methyl-4-nitroaniline hydrochloride, and then dilute the hydrochloride with water to obtain 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline. , the highest yield is 59.4%, and the purity is over 99%. The improved method is easy to control the nitrification reaction temperature, has no special requirements for equipment and operations, and is more suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Apply[2]
2-Methyl-6-nitroaniline is widely used in modern chemical production, such as rubber manufacturing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, printing and dyeing manufacturing and other industries.
Preparation [2-4]
Method 1:
Step 1: Acetylation of o-toluidine:
1) Direct acetylation. Add 100 mL acetic anhydride to a 250 mL three-necked flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, thermometer and constant pressure dropping funnel, and add 53.5 mL o-toluidine dropwise at room temperature. The addition rate should be such that the system temperature does not exceed 40°C. After the addition is completed and the reaction continues for 0.5 h, cool to below 10°C. A solid will gradually precipitate. Filter it to obtain a white solid. Use NaOH solution to adjust the mother liquor to pH = 8 ~ 9. A small amount of white solid will precipitate. Filter and combine the filter cakes. Vacuum A total of 62.6 g of white solid was obtained after drying, which was identified as 2-methylacetanilide with a yield of 84%.
2) Catalytic acetylation: Add 60 mL acetic anhydride and 21.65 g lanthanum nitrate hexahydrate into a 250 mL three-necked flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, thermometer and constant pressure dropping funnel, and add 53.5 mL o-methane dropwise at room temperature. aniline. The feeding rate should be such that the temperature of the system does not exceed 40°C. After the addition is completed, the reaction continues for 0.5 h. The reaction solution was cooled to below 10°C, and a white solid gradually precipitated. It was filtered and dried under vacuum to obtain a total of 64.5 g of white solid, which was identified as 2-methylacetanilide with a yield of 86.6%.
Step 2: Nitration of 2-methylacetanilide: Add 240 mL acetic anhydride and 30 mL acetic acid to a 500 mL three-neck flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, thermometer and constant pressure dropping funnel, and control the temperature at 10 ~ At around 12°C, add 63 mL concentrated nitric acid dropwise. After the dropwise addition is completed, add 74.5 g of solid 2-methylacetanilide in batches. The addition rate should strictly control the system temperature at 10 to 12°C. After the addition, continue the reaction for about 0.5 hours until the temperature no longer rises. Then pour the material. Pour into 1500 mL of ice water. A large amount of light yellow solid will precipitate. Stir and filter to obtain a light yellow solid. Dry and set aside.
Step 3: Hydrolysis and post-treatment of 2-methylacetanilide nitration product. Transfer the above light yellow solid to a 500 mL flask, add 150 mL of 36% to 38% concentrated hydrochloric acid, and heat to reflux in a water bath for 3 seconds with mechanical stirring. A dark red solution was obtained, and a small amount of orange-yellow solid precipitated. Then cool to room temperature, pour 750 mL of ice water into the above dark red material, continue stirring for 30 minutes, a large amount of orange solid precipitates in the middle, filter, wash 3 times with 100 mL distilled water, and dry the filter cake to obtain 51.1 g of orange solid. Crude solid product, mother liquor is dark red. The obtained crude product was recrystallized with 125 mL of ethanol [φ(CH3CH2 OH)=95%] to obtain 46 g of orange-red needle-like crystals, which were identified as 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline. Melting point 94 ~ 96 ℃ (literature value 95 ~ 96 ℃, yield 59.4% (based on 2-methylacetanilide).
Method 2:
Step 1: Acetylation of o-toluidine
The optimization of the synthesis process of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline breaks through the traditional hydrochloric acid mixing process and uses nitration reaction to control the temperature. As a result, the synthetic material of p-2-methyl-6-nitroaniline is In the preliminary treatment, acylation is first used for component treatment, and then the product is synthesized, and o-toluidine is directly acylated. After directly fusing it with concentrated nitric acid, o-toluidine will generate 2-methylacetanilide, and the reaction proportion of the original substance is determined to be 80%; secondly, it is catalyzed with the help of acetic anhydride and hexahydrate lanthanum nitrate, and after cooling and drying Finally, 89.5% of 2-methylacetanilide was recovered. After two reaction treatments, a large proportion of the o-toluene component in the raw material was initially extracted.
Step 2: Acidification treatment of 2-methylacetanilide. Take the 2-methylacetanilide product extracted from this experiment, add acetic anhydride and acetic acid reaction materials in a ratio of 1:2, and adjust the reaction temperature to Control it at around 15°C, and then gradually add 20mL of concentrated nitric acid. After the substance in the bottle reacts completely, use ice water to cool down the solution. After preliminary solution treatment, filter out the solid matter in the solution, dry it and seal it for collection.
Step 3: Dissolve the 2-methylacetanilide product. Put the material after the reaction of 2-methylacetanilide with acetic acid and acetic anhydride into concentrated hydrochloric acid. At this time, the proportion of the material and liquid is 10:3 , then stir the two substances thoroughly. When the stirred liquid turns dark red, separate the solution from the yellow solid and place it in a cooling environment for about 5 to 10 minutes. Continue to add ice water to the discolored liquid and continue stirring until the solution appears during stirring. When yellow solid objects appear, stop stirring.
Finally, the product after the 2-methylacetanilide compound reaction is treated by distillation, and the solid is washed with an ethanol solution with a concentration of 50% to obtain 2-methyl-6- Nitroaniline. In order to further verify the qualification of the produced items, the extracted 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline was tested. The relevant values are: melting point of 135°C, H NMR (400MHz, CDCl3), CH on the benzene ring The quantities are 3,200 and 2,900, which are within the qualified control range of its composition compared with the reference value for the synthesis of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline.
Method 3: Using o-nitroaniline as raw material, undergo acetylation reaction, methylation reaction, and finally hydrolysis to obtain 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline. The reaction steps are simple, no strong acidic substances are used, the requirements for production equipment are not high, the temperature is easy to control, and the operation is simple and convenient. The yield of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline synthesized by this method is as high as 93.9%, which greatly improves the yield, and the product purity is 99.6%, which meets market demand and is suitable for industrial large-scale production. The synthetic route of the target product is as follows:
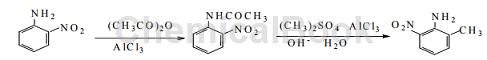
Step 1: Install a stirrer, dropping funnel and thermometer on the 250 mL three-necked flask. Quickly weigh 16.0 g of finely ground anhydrous AlCl3, put it into the flask, and immediately add 13.8 g of o-nitroaniline and 30 mL of diethyl ether. Shake the flask evenly to dissolve it completely. Then use the dropping funnel to add 9.45 mL of acetic anhydride dropwise. After dripping, close the drip funnel cock, heat on a small fire on an asbestos mesh, and maintain slow reflux at a certain temperature for several hours.
After the reflux is completed, immerse the three-necked flask in cold water and let it cool. Orange-yellow needle-like crystals will precipitate. Filter at room temperature and wash the obtained filtrate with distilled water. Three times, the crude product was dried, leaving about 17.8 g of crude product. Dissolve the crude product in distilled water, heat the solution, cool and recrystallize to obtain 17.4 g of pure o-nitroacetanilide, yield 96.7%, mp 74-76°C, purity 99.5%.
Step 2. Add 17.4 g of o-nitroacetanilide and 30 mL of ether synthesized in the previous step into a 250 mL three-necked flask, quickly weigh 16.0 g of finely ground anhydrous AlCl3, and install a stirrer and a dropping funnel respectively. and thermometer. Then add 9.17 mL dimethyl sulfate to the dropping funnel. After dripping, close the drip funnel cock, heat on a small fire on an asbestos mesh, and maintain slow reflux at a certain temperature for several hours.
Then immerse the three-necked flask into cold water, and slowly add 19.34 mL of 20% NaOH solution dropwise while stirring. Leave to cool, and yellow prism crystals will precipitate. Filter under normal temperature. The obtained filtrate is washed three times with 20 mL of 20% NaOH solution and 20 mL of distilled water. The crude product is dried, and about 14.5 g of crude product is retained. Dissolve the crude product in distilled water, heat the solution, cool and recrystallize to obtain 14.3 g of pure 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline, yield 97.2%, mp 95~97°C, purity 99.6%.
Main reference materials
[1] Research on the synthesis process of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline
[2] Synthesis process of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline
[3] Synthesis and characterization of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline
bucket and thermometer. Then add 9.17 mL dimethyl sulfate to the dropping funnel. After dripping, close the drip funnel cock, heat on a small fire on an asbestos mesh, and maintain slow reflux at a certain temperature for several hours.
Then immerse the three-necked flask into cold water, and slowly add 19.34 mL of 20% NaOH solution dropwise while stirring. Leave to cool, and yellow prism crystals will precipitate. Filter under normal temperature. The obtained filtrate is washed three times with 20 mL of 20% NaOH solution and 20 mL of distilled water. The crude product is dried, and about 14.5 g of crude product is retained. Dissolve the crude product in distilled water, heat the solution, cool and recrystallize to obtain 14.3 g of pure 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline, yield 97.2%, mp 95~97°C, purity 99.6%.
Main reference materials
[1] Research on the synthesis process of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline
[2] Synthesis process of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline
[3] Synthesis and characterization of 2-methyl-6-nitroaniline

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

