Background and issues[1][2]
Add 0.5g of ordinary commercially available water-soluble florfenicol (70% content) to 50 ml of water and stir at room temperature. It is basically insoluble. It can be completely dissolved after heating to 70°C, and more crystals will precipitate after cooling. The soluble powder made from it does not meet the quality standards of soluble powder, and it cannot be made into water-injection preparations. In order to improve the bioavailability of the drug and change the route of administration, dimethyl sulfoxide and other solvents are used as solvents to make terflorfenicol injections on the market. However, the cost is high, the pharmaceutical excipients have serious side effects, and are not conducive to the absorption of the drug. Compared with soluble powder In comparison, the drug utilization rate was not significantly improved. In order to improve the efficacy, facilitate combined use with other antibiotics, reduce the dosage, and reduce the residues of veterinary drugs in meat products, there is an urgent need to prepare truly water-soluble florfenicol.
Florfenicol, also known as thiamphenicol and thiamphenicol, is the 3-position fluorine derivative of thiamphenicol among the broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs of the chloramphenicol class. Florfenicol can be used to treat cattle respiratory diseases caused by Pasteurella and Haemophilus. It has a good effect on cattle foot rot caused by Fusobacterium. It can also be used to treat pig and chicken infections caused by sensitive bacteria. Diseases, such as pigs exposed to infectious pleuropneumonia, etc. Florfenicol is a new antibiotic specially used in the animal health market. Its biggest feature is its broad antibacterial spectrum, good absorption, wide distribution in the body, and especially its lack of potential to cause aplastic anemia.
Florfenicol is a structural homologue of chloramphenicol (Chloramphenicol). Its mechanism of action and antibacterial spectrum are similar to those of chloramphenicol and thiamphenicol, but florfenicol does not produce similar chloramphenicol and thiamphenicol. Mycin plasmid-mediated resistance and many chloramphenicol-resistant strains remain susceptible. Because chloramphenicol has serious adverse reactions that can cause aplastic anemia, many countries have banned its use in animal disease prevention and treatment, especially in food-producing animals. Therefore, florfenicol will replace chloramphenicol in the prevention and treatment of animal diseases, especially food animals, and has broad application prospects in veterinary clinical practice. Florfenicol is insoluble in water, and in many cases it is necessary to make water-soluble florfenicol.
Preparation method【3】
1. Physical methods
1. The package is legal.
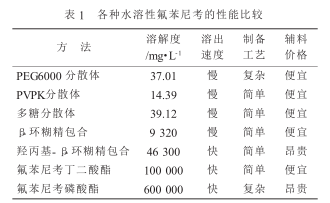
The inclusion method refers to a drug molecule being trapped in the hole structure of another molecule to form an inclusion complex to improve the solubility and stability of the drug. Wei Xiaozang et al. used a saturated solution method to prepare florfenicol-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex, which increased the solubility of florfenicol in water from 1.41 mg/ml to 9.32 mg/ml. Solubility is greatly improved. Deng Libin et al. prepared it into florfenicol-2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex, which increased the solubility of florfenicol 35.6 times (from 1.3 mg/ml to 46.3 mg/ml) .
2. Dispersion method.
The dispersion method is a new technology that highly disperses poorly soluble drugs in another solid carrier, which can improve the dissolution rate and solubility of poorly soluble drugs. Hong Tao et al. used solid dispersion technology solvent method to successfully prepare florfenicol solid dispersion using PVPK as a carrier, which increased the solubility of florfenicol by 13.0 times and significantly increased the dissolution rate.
Wang Duxue used polyethylene glycol 6000 as a carrier and used a melting method to prepare a solid dispersion. The cumulative drug dissolution rate of this solid dispersion reached 76.80% at 20 minutes, indicating that polyethylene glycol 6000 p-fluorfenil It has obvious dissolving effect. Liu Yang et al. used a solvent-free melting method to prepare florfenicol solid dispersion using polyethylene glycol 6000 as the carrier. The dissolution rate of the solid dispersion was higher than that of florfenicol original powder and physical mixture, and the solubility of the solid dispersion reached 3.441 mg/ml.
3. Micronization.
Liu Yongqiong et al. selected oligosaccharide excipients and used spray drying method to prepare florfenicol soluble powder. The dissolution rate and dissolution percentage of the soluble powder obtained by spray drying is significantly higher than that of the physical mixture. Its dissolution rate of 99.05% is 42.15 times that of the raw material florfenicol (dissolution rate 2.35%), which greatly improves the water solubility of florfenicol. .
Wang Anguo et al. Mix PVPK30, SDS, and florfenicol evenly, crush them, pass them through a 150-mesh sieve, then add anhydrous glucose, mix evenly, and prepare water-soluble compound florfenicol micropowder. The particle size of micronized florfenicol is finer and more uniform, so the surface area is increased, the porosity is increased, and the adsorption and solubility are enhanced. The drug can be better dispersed and dissolved in the gastric juice, increasing the contact with the gastric mucosa. area, thereby making it easier to be absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract, greatly improving bioavailability.
2. Chemical methods
The structure of florfenicol was modified and transformed to produce a prodrug of florfenicol, which greatly improved its water solubility. 1. Florfenicol phosphate. Florfenicol phosphate developed by Schering-Plough has a sodium salt solubility as high as 700 mg/ml, excellent pharmacokinetic properties, and high bioavailability, and can be easily made into water-based injections. However, the synthesis reaction conditions of this product are harsh, and the required reagents are expensive and difficult to obtain, making it unsuitable for industrial production. 2. Florfenicol succinate.
Qin Guangcheng reported florfenicol succinic acid monoester and its preparation method. Florfenicol succinic acid monoester can be obtained by the esterification reaction of florfenicol and succinic anhydride; florfenicol succinic acid monoesterPharmaceutically acceptable salts of hydroxy acid monoesters such as sodium salt, potassium salt, calcium salt and magnesium salt, etc., as well as salts formed with basic amino acids include lysine salts and arginine salts, with water solubility greater than 500 mg/ ml. This type of water-soluble derivative rapidly releases florfenicol after hydrolysis in the body and can be used as a highly water-soluble prodrug of florfenicol.
Liu Zhelin et al. synthesized amber florfenicol through esterification reaction, that is, florfenicol succinic acid monoester is the prodrug of florfenicol, which can be metabolized into florfenicol in animals, and its sodium The water solubility of the salt is 100 mg/ml. 3. Florfenicol and nitric acid complex. Peng You et al. used 13 g of florfenicol, added 15 ml of dilute nitric acid of appropriate concentration, heated to 40°C to 50°C, stirred to dissolve, and left to stand for about 12 hours. Add an appropriate amount of propylene glycol and stir for about 2 hours, filter, wash the filter cake with an appropriate amount of ethanol, and dry to obtain 13.6 g of white water-soluble florfenicol with a solubility of 1.7 g. It can be used as a raw material for water injections, with greatly reduced costs and better water solubility.
References
[1] Peng You, Xie Baohua, Deng Zeyuan, Huang Youhui. Research on the preparation of new water-soluble florfenicol [J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008(08):3237-3239.
[2] Liu Zhelin, Yin Hongxi, Wang Xiaojie, Li Chunjie, Lu Shurong. Research progress on water-soluble florfenicol [J]. Veterinary Drugs and Feed Additives, 2007(06):8-9.
[3]Liu Hongliang. Research on water-soluble florfenicol[J]. Veterinary Guide, 2017(19):44-45.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

