[Background and Overview][1][2]
Chemical formula of m-bromophenol is C6H5BrO, molecular weight 173.00700, CAS number 91-20-8, white to off-white solid, density 1.63 g/cm3, melting point 30 °C, boiling point 236 °C (lit.), flash point 236 °C (lit.), refractive index 1.595-1.599, easily soluble in water, can be used as an organic synthesis intermediate, Solvent. Meta-bromophenol is the raw material for the synthesis of non-morphine powerful analgesic tramadol hydrochloride, triarylmethanethiophene anti-tuberculosis drugs and 4-arylpiperidine anti-itch drugs. The traditional synthesis method of m-bromophenol uses nitrobenzene as raw material and is produced through bromination, reduction, diazotization and hydrolysis, with a total yield of 12%. It can also be obtained by diazotization and bromination of meta-aminophenol. Dissolve m-aminophenol in sulfuric acid, cool to below 10°C, and add sodium nitrite aqueous solution dropwise. After diazotization reaction, filter, and the filtrate is hydrolyzed with cuprous bromide. Then distill, collect the evaporated liquid, add salt and filter, the filtrate is extracted with diethyl ether, the extract is dried, the diethyl ether is recovered by distillation, and m-bromophenol is distilled out. If m-bromophenol is inhaled, move the patient to fresh air; in case of skin contact, take off contaminated clothing, rinse the skin thoroughly with soap and water, and seek medical treatment if you feel uncomfortable; if eye contact occurs, separate eyelids , rinse with running water or normal saline, and seek medical attention immediately; if ingested, rinse mouth immediately, do not induce vomiting, and seek medical attention immediately.
[Application][2][3][4]
M-bromophenol is an organic synthesis intermediate and a raw material for pesticides and medicines. It can be used to synthesize m-bromoanisole; it is also a synthetic antibiotic. The main intermediate of the cancer sedative and analgesic drug tramodol, and can be used in other medicines, dyes and organic synthesis. Meta-bromophenol is the raw material for the synthesis of non-morphine powerful analgesic tramadol hydrochloride, triarylmethanethiophene anti-tuberculosis drugs and 4-arylpiperidine anti-itch drugs. Examples of its applications are as follows:
1. Used to synthesize m-bromoanisole, including the following process steps,
a. Select a 1000L reactor as the reaction vessel.
b. Weigh 390-410kg sodium hydroxide solution and 490-510kg m-bromophenol solution and place them in the reaction vessel in step a, and start stirring to dissolve the mixture.
c. Pour steam into the jacket of the mixed material after stirring in step b to heat it, and control the temperature in the kettle to 55-65°C.
d. Continue to stir the mixture in the kettle, and add 350-400kg of dimethyl sulfate dropwise while stirring. Complete the dropwise addition of dimethyl sulfate within 2.5-3.5h. After the dropwise addition is completed, continue the reaction for 2.0 h.
e. Cool the product obtained after the reaction in step d, and then put the cooled product into an oil-water separator and let it stand for 4.0 hours to separate the oil layer and the water layer.
f. Take out the oil layer in step e for later use, extract the water layer with 190-210kg of diethyl ether, dry the extracted diethyl ether layer with anhydrous calcium chloride and put it into a still for distillation.
g. Combine the residue after distillation in step f with the oil layer to be used and put it into a rectification tower for vacuum distillation. The collected fraction is the finished product of m-bromoanisole.
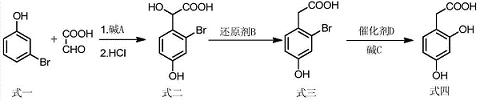
2. Used to synthesize 2,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid. The preparation method is to use m-bromophenol and glyoxylic acid as starting materials, a condensation reaction occurs in an alkaline solution, and after acidification, p-hydroxy ortho-bromide is obtained. Mandelic acid, p-hydroxy-o-bromomandelic acid is further reduced by a reducing agent to obtain p-hydroxy-o-bromophenylacetic acid, p-hydroxy-o-bromophenylacetic acid is catalyzed by a catalyst in an alkaline solution to undergo a hydroxylation reaction of bromine, and after acidification, 2,4- Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid specifically includes the following steps:
(1) In the solution of base A, m-bromophenol (structural formula 1) and glyoxylic acid are used as raw materials, and a condensation reaction occurs at a certain temperature; after the reaction is completed, cool to room temperature and acidify to pH with concentrated hydrochloric acid =1, then wash with toluene, extract with ethyl acetate, and concentrate to obtain 2-bromo-4-hydroxymandelic acid (structural formula 2);
(2) Mix 2-bromo-4-hydroxymandelic acid and reducing agent B, stir and heat for a certain period of time; after the reaction is completed, pour into water, heat to dissolve, cool to room temperature, filter, wash and recrystallize , obtaining 2-bromo-4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (structural formula 3);
(3) 2-Bromo-4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid is reacted in a solution of base C and in the presence of catalyst D at a certain temperature; after the reaction is completed, it is cooled to room temperature, filtered, and the filtrate is collected. The filtrate is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid Acidify to pH=3, filter, wash and recrystallize to obtain 2,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
【Preparation】[1]
M-Bromonitrobenzene uses a phase transfer catalytic method to synthesize m-bromoanisole in one step, and then demethylates it to prepare m-bromophenol, with a total yield of 32%. The specific steps are as follows:
1) Synthesis of m-bromonitrobenzene
Take 12.3 g (10.20 mL 0.1 moL) of nitrobenzene and 12.3 g (81.56 mL) of 66% sulfuric acid, heat it in a water bath at 30-35 ℃, and slowly add 15 g (0.1 moL) of sodium bromate in batches. The color will change from light to light. Red-yellow turns into light yellow. When it turns light yellow, continue to add sodium bromate until the addition is complete, react for another 4 hours, and crystal grains appear. After the reaction, the orange-red crystals were taken out, washed with a large amount of water, and then recrystallized with ethanol to decolorize the activated carbon to obtain 16 g of light yellow crystals with a yield of 79%.
2) Synthesis of m-bromobenzyl��
Take 40 mL of cyclohexane, 3.84 g of methanol (0.12 moL), 15.8 g of solid potassium hydroxide (0.28 moL) and 5.05 g (0.018 moL) of phase transfer catalyst tetrabutylammonium chloride (PTC) and add it to the belt In a three-necked flask with a stirrer, 100 mL of cyclohexane solution containing 18.1 g (0.09 molL) of m-bronitrobenzene was added dropwise at 55 °C, and then reacted at 60 °C for 2.5 h. Air should be continuously bubbled into the reaction system. Cool, wash with water, wash away tetrabutylammonium chloride with hydrochloric acid solution, wash with water again, and dry with anhydrous MgSO4. The solvent was rotary evaporated to obtain 13.7 g of light yellow liquid, with a yield of 81.4%.
3) Synthesis of m-bromophenol
Put 10 g (0.087 mol) of the prepared pyridine hydrochloride solid into a flask, take 3 g (0.016 mol) of m-bromoanisole, and stir for 5 h under closed nitrogen protection at 190°C. After the reaction system is cooled, pour the reaction solution into a small amount of alkali solution and stir in an ice bath. Impurities were extracted with methylene chloride. Add acid to the aqueous layer to adjust the pH. When the pH is close to neutral and slightly acidic, a brown oily precipitate will appear. Extract the product with dichloromethane, dry it with anhydrous MgSO4 for 24 h, filter the extract and remove the dichloromethane by rotary evaporation to obtain the final product m-bromophenol 1.4 g, yield 50%,
[Main reference materials]
[1] Wang Jing, Zhang Xiaopeng, Yang Bo. Improvement of m-bromophenol synthesis process[J]. Applied Chemical Engineering, 2010, 39(6): 934-935.
[2] Fan Peiren; Fan Bin; Zhu Junfei; Chen Xinzhi; Li Yinge; Liu Wei. A production method and production device of m-bromophenol. CN200710066702.X, application date 2007-01-15
[3] Zhang Xueyong; Lu Jianxin; Jin Min; Zhang Guangsheng. A production process for the synthesis of m-bromoanisole. CN201410242523.7, application date 2014-06-03
[4] Zou Yong; Xu Tianlong; Wei Wen; Sheng Jianfei; Wei Wentao. A preparation method of 2,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid. CN201511022024.8, application date 2015-12-29

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

