Background and overview[1]
Sodium ferric oxalate is also known as “sodium trioxalatoferric(III)ate”. Chemical formula Na3[Fe(C2O4)3]·xH2O. Molecular weight 365.89. Green monoclinic crystal. Relative density 1.93717.5. When heated to 100~120℃, 1 molecule of water begins to be lost. Add excess sodium oxalate to the Fe3+ solution and evaporate and crystallize to obtain sodium ferric oxalate.
Preparation[1]
Method 1: Step-by-step recovery of magnesium, iron and aluminum from vanadium-containing solutions. The vanadium-containing solution described in this embodiment is: the vanadium concentration is 1-6g/L; the magnesium concentration is 1-6g/L; the iron concentration is 3-13g/L; the aluminum concentration is 5-30g/L; and the oxalate concentration is 100~300g/L.
Step 1) According to the material ratio of sodium ions in the sodium salt: iron ions in the liquid after magnesium removal is (3-6): 1, add the sodium salt into the liquid after magnesium removal, at 50~ Stir for 1 to 2 hours at 60°C to obtain the reaction liquid I.
Step 2) Crystallize the reaction liquid I at 0 to 10°C and in the dark for 24 to 36 hours, and separate the solid and liquid to obtain the iron-removed liquid and crystal I.
Step 3) According to the liquid-to-solid ratio of (1-1.5) m3/Kg, add water at 90-100°C to the crystal I, stir until completely dissolved, cool, and then place at 0-10°C and avoid Recrystallize under light conditions for 12 to 18 hours, separate solid and liquid, and obtain filter cake II.
Step 4) Wash the filter cake II with deionized water at 0 to 10°C 4 to 5 times, and dry it to obtain sodium ferric oxalate (Na3[Fe(C2O4)3]·3H2O).
Method 2: A saponification-free method for stripping iron of loaded organic extractants:
(1) Prepare sodium oxalate solution: first open the pure water valve and pure water pump, add pure water to the sodium oxalate preparation tank, then add sodium oxalate, prepare a sodium oxalate solution with a concentration of 25g/l, and stir for half an hour Then pour it into the low-level sodium oxalate tank for later use.
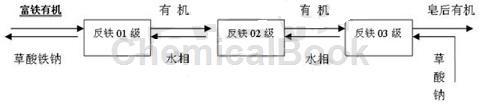
(2) Back extraction: As shown in Figure 1, it is a flow chart of the saponification-free iron stripping method. The iron-rich organic extractant P204 (iron ion content is 15g/l) enters the extraction box from anti-iron 01 level. , at the same time, the sodium oxalate solution enters from the sodium oxalate low-level tank through the anti-iron 03 stage. The flow ratio of the sodium oxalate solution to the organic extractant loaded with iron ions is 2.9:1. After three-stage stripping, the saponified organic extractant is obtained. After entering the system for recycling, sodium ferric oxalate is discharged from the system through the water phase and can be taken away as a by-product. During specific use, the anti-iron series can be set according to the iron content in the organic matter. After stripping the iron-rich organic extractant, Fe is less than 15 mg/l.
Main reference materials
[1] Compound Dictionary
[2] CN201910262221.9 A method for stepwise recovery of magnesium, iron and aluminum from vanadium-containing solution

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

