P-bromoxynil, also known as 4-bromoxynil, is an important bromine-based fine chemical, mainly used in the fields of medicine and organic synthesis.
Synonyms: 4-bromoxynil; P-bromoxynil
Molecular formula: C7H4BrN
CAS No: 623-00-7
Molecular weight: 182.02
Melting point: 111-114℃
At present, there are still no literature reports on the synthesis process of p-bromoxynil in China, let alone a manufacturer. This article discusses the synthesis route of p-bromobenzaldehyde and hydroxylamine hydrochloride to produce p-bromobenzaldehyde oxime, and then cyanation reaction with formic acid to obtain p-bromoxynil. Based on the original foreign synthesis route, each process parameter is further optimized. , obtain the best reaction conditions, and provide necessary, true and reliable operating processes and parameters for industrial production.
Synthesis of p-bromobenzaldehyde oxime
Add p-bromobenzaldehyde, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and water in a certain proportion into a flask with a stirrer, condenser and thermometer, heat and stir at 70-75°C React for 1 hour. Cool, filter, and dry to obtain a white solid, which can be used in the next experiment. The solid purity reached 99.2% by gas chromatography.
Synthesis of p-bromoxynil
P-bromobenzaldehyde oxime and formic acid dried by anhydrous sodium sulfate are put into a mixer, condenser and Thermometer in flask,
Reflux under stirring for 1.5 h, cool, filter, and wash the filter cake until neutral to obtain a white solid with a purity of 99.3% after testing. The formic acid filtrate is mixed multiple times and then distilled under normal pressure to collect the 100°C-105°C fraction, which can be recycled after drying with anhydrous sodium sulfate.
Comparison with the original method
The synthesis method reported in the original literature is to stir p-bromobenzaldehyde, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and formic acid (98%) together at room temperature for half an hour, and then add a large amount of cold water to precipitate the p-bromobenzaldehyde. Bromoxynil, filtered to obtain product L7 J. There are three disadvantages in this method: First, at the given temperature and time, the reaction cannot proceed completely, and the obtained product contains the raw material p-bromobenzaldehyde, which is difficult to purify. Second, the one-pot reaction requires formic acid to have a low water content, and commercially available formic acid is generally 85% to 89%, which has a large water content, and 98% formic acid is difficult to obtain. Third, the reaction mixture is poured into a large amount of water, making it difficult to recover formic acid. The reaction mixture is diluted with cold water about 10 times the mass of formic acid. After filtering to obtain the product, the formic acid content of the filtrate is very low, and the cost of recovery and recycling is high, making it unsuitable for industrialization.
In view of the above shortcomings, this article has made improvements and achieved better results. First, this article changed the experiment from a one-pot method to a two-step method. First, p-bromobenzaldehyde oxime was obtained, dried, and then reacted with formic acid. The reaction between p-bromobenzaldehyde oxime and formic acid is reversible, and the water content in the reaction mixture decreases
less, the reaction equilibrium shifts toward the product. Therefore, reducing the amount of water during the reaction will promote the reaction. Since the reaction between p-bromobenzaldehyde and hydroxylamine hydrochloride can produce water, the reaction is as follows:
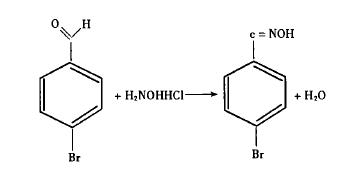
After the reaction is divided into two steps, the influence of the water generated in this reaction on the next reaction can be eliminated by drying the product of the first step, p-bromobenzaldehyde oxime, so that Formic acid gives good results at a purity of 95.3%. Secondly, after the second step of the experiment, cool the reaction mixture with ice water, and needle-like crystals of p-bromoxynil will precipitate. Filter, wash with water, and dry to obtain a product with a yield of 98.8% and a purity of 99.3%. , and the formic acid filtrate is also easy to recover and recycle, which greatly saves costs. In addition, commercially available formic acid with a purity of 89% was treated with anhydrous sodium sulfate to make it meet the requirements of this reaction, which is also the originality of this article. Sodium sulfate can be recycled after treatment.
Final synthesis conclusion
The best process for producing p-bromobenzaldehyde oxime by reacting p-bromobenzaldehyde with hydroxylamine hydrochloride, and then cyanating it with formic acid to obtain p-bromoxynil
The parameters are: p-bromobenzaldehyde: hydroxylamine hydrochloride: formic acid = 9.25: 4.5: 55 (mass ratio), oximation reaction temperature is 70-75°C, time is 60 minutes, cyanide
The reaction temperature was reflux temperature and the reaction time was 1.5h. The purity of p-bromoxynil obtained was 99.3%, and the yield was 98.7%.
For more information, please refer to: Research on the synthesis process of p-bromoxynil

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

