Background [1][2]
Styrene is insoluble in water and easily soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, acetone and benzene. It can slowly polymerize and oxidize in the air. It is necessary to add polymerization inhibitors such as catechol during storage, and the addition reaction of olefins can also occur. A colorless, transparent liquid with a strong aroma. Insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol and ether. It can polymerize and copolymerize with other monomers. Used in the manufacture of resins, plastics, synthetic rubber, etc. It is obtained by catalytic dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene, or by extractive distillation of the carbon eight fraction of cracked tar.
Polystyrene products such as food preservation utensils often release styrene, which may also accumulate in food and contaminate the food, causing it to taste bad. Animal experiments on guinea pigs and rabbits, and styrene workshop workers inhaling styrene (air with a concentration of 10 to 50 mg/m3) are excreted in the urine in the form of phenylglycolic acid and do not accumulate in the body. It is a low-toxic compound in acute effects.
The allowable concentration in the working environment air is: 100ppm (425mg/m3) in the United States, 50ppm (210mg/m3) in Japan, and 5mg/m in the Soviet Union3. The concentration specified in the air quality standards: the Soviet Union, Bulgaria and Yugoslavia are 0.0007ppm (0.003mg/m3, averaged over 24 hours and 0.5 hours), and the Federal Republic of Germany is 4.6ppm (20.0mg/m3 , long-term standard), 15.16ppm (65.0mg/m3, short-term standard). Our country stipulates that the maximum allowable concentration in the atmosphere in residential areas is 0.01mg/m3 (one time).
Synthetic route [3][4]
Prepared from ethylbenzene or phenethyl alcohol[1]. Install a 24cm fractionating column on a 500ml flask, place 148g of dry cinnamic acid, 2g of hydroquinone and a few pieces of clay in the flask, and then place 0.5g of hydroquinone in the flask that collects the distillate . Heat until styrene begins to distill off, and then adjust the temperature to 120°C for the steam in the fractionating column. After 3.5-5 hours, separate the distillate into layers, add 100 ml of water, and then distill the water-containing mixture. Then separate the oil (45-48g), dry it with a small amount of calcium chloride, and distill it under reduced pressure. During distillation, the condenser and receiver must be cooled to 0-5°C with ice water, and the 44-46°C/5332Pa distillate is collected. portion, the product is 40-42g.
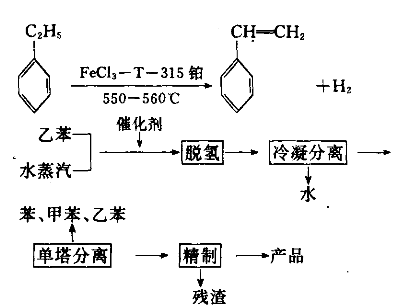
Method 2: Use waste polystyrene and styrene tar to make styrene. This is achieved by cracking the raw material (styrene tar or waste polystyrene plastic) and then distilling and rectifying it to obtain styrene monomer. The process is described below: 1) Cracking: Put waste polyethylene plastic or styrene tar into the cracking kettle, ignite it and raise the temperature to control the temperature in the kettle between 320 and 400°C to produce crude styrene monomer. ;
2) Distillation: Put the crude styrene monomer obtained above into the distillation kettle, control the temperature within the range of 80 to 110°C, and control the vacuum within the range of 550 to 650mmHg to obtain a content of 70% by distillation Styrene monomer above. The styrene monomer can be directly used in the production of styrene modified resin and other industries. 3) Distillation: After distillation, the product is rectified through a distillation tower and the 145-147°C fraction is intercepted to obtain a product with a content of more than 99%.
Production status and forecast[7]
From 2013 to 2016, global styrene production capacity increased by 5.9%. In 2016, the production capacity was 34.005 million t/a, mainly concentrated in the Asia-Pacific region (17.839 million t/a, accounting for 52.49%) and North America (592.5 million t/a, accounting for 17.42%), Western Europe (5.165 million t/a, accounting for 15.19%). It is predicted that by 2020, the global styrene production capacity will exceed 37 million t/a, and China, as the world’s largest styrene producer, will play a major role in this. In recent years, no large-scale styrene equipment has been put into operation abroad, nor are there plans to build new or proposed equipment. Existing styrene companies have been shut down and reorganized to better integrate resources.
NihonOxirane Company’s 420,000 t/a styrene plant located in Chiba, Japan, announced its permanent shutdown in May 2015; while Asahi KASEI Company’s 320,000 t/a styrene plant located in Mizushima, Japan a The styrene unit was also closed in March 2016; SIBUR Group transferred its equity in its styrene industry due to strategic development needs.
Apply[1][5][6]
Styrene is an important industrial raw material and a monomer for the preparation of plastics, resins and synthetic rubber. Its self-polymerization can produce polystyrene resin, and it can also be copolymerized with many other unsaturated compounds to produce a variety of engineering plastics and rubbers for different uses, such as acrylonitrile (A), butadiene (B) and styrene (S) , trimerized to produce ABS resin, which is widely used in various household appliances and industrial instruments; styrene is copolymerized with a small amount of p-divinylbenzene, and then sulfonated to produce styrene-type acidic cation exchange resin; styrene and butadiene The copolymerization of styrene and acrylonitrile produces styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) that is resistant to aging, oil, and wear, and its output ranks first in synthetic rubber; the copolymerization of styrene and acrylonitrile produces SAN resin that is impact-resistant and bright in color. A small amount of styrene is used as a raw material for synthetic fragrances.
1. Prepare a styrenic flame retardant resin composition.
The composition of the flame-retardant styrenic resin composition is as follows: with respect to 100 parts by mass of rubber-modified polystyrene resin (A), 5.5 to 12 parts by mass (B) containing 2, 4, Bromine flame retardant of 6-tris(2,4,6-tribromophenoxy)-1,3,5-triazine, 0.5~5 parts by mass (C) flame retardant auxiliary, and 0.5~1.6 parts by mass Part (D) lubricant, said (D) lubricant is selected fromTwo or more types of the group consisting of (a) polyolefin wax, (b) higher fatty acid amide, and (c) higher carboxylic acid metal salt.
Wherein, the respective ratios of (D) lubricants are: (a) 0 to 40 mass %, (b) 0 to 80 mass %, and (c) 0 to 80 mass %, (a), The total amount of (b) and (c) is 100% by mass. A resin composition that has excellent product strength (screw loosening torque after assembly and detachment), and excellent balance between moldability (fluidity, mold release, scratch resistance), and heat resistance (deflection temperature under load). The advantages contribute to the thinning of toner cartridge containers used as internal components of printers, FAX machines, and copiers, and their industrial utilization value is very high.
2. Preparation of benzaldehyde, styrene oxide and styrene cyclic carbonate.
The products of oxygen oxidation of styrene are mainly styrene oxide and benzaldehyde, both of which are widely used as intermediates in the synthesis of fine chemicals. Among them, due to the presence of active epoxy groups, styrene oxide can react with a variety of substances to form high value-added compounds, which are used in spice production, drug preparation and other fields, such as the preparation of spices β-phenylethanol and gamizoles; benzaldehyde It can be used to synthesize food additives such as L-phenylalanine. In recent years, with the sharp growth in demand for such fine chemical products, styrene oxide and benzaldehyde have attracted much attention both in industrial production and organic synthesis.
The method includes the following steps: A) Mix styrene, a solvent and a catalyst, and add an oxidant to perform an oxidation reaction to obtain a reaction liquid and a mixed gas. The reaction liquid contains benzaldehyde and styrene oxide, and the The mixed gas contains formaldehyde; B) separate the reaction liquid to obtain benzaldehyde and styrene oxide; C) catalytically oxidize the mixed gas to convert formaldehyde into carbon dioxide and water; and D) make the mixture containing The mixture of carbon dioxide reacts with a portion of the styrene oxide to form styrene cyclic carbonate.
Main reference materials
[1] Encyclopedia of Chinese Middle School Teaching·Chemistry Volume-
[2] Dictionary of Environmental Science
[3] Synthetic fragrance product technical manual
[4] CN88103864.4 Making styrene from waste polystyrene and styrene tar
[5] CN201180062450.8 Flame-retardant styrene resin composition and toner cartridge container using the same
[6] CN201610712469.7 Method and device for styrene oxidation to co-produce benzaldehyde, styrene oxide and styrene cyclic carbonate
[7] Tao Xiaoyu, Gong Chao, Li Quan, et al. Styrene market analysis and outlook[J]. Chemical Industry, 2018, 36(1): 38-42.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

