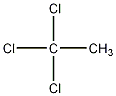
Structural formula
| Business number | 01GL |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H3Cl3 |
| Molecular weight | 133.40 |
| label |
Methyl chloroform, α-Trichloroethane, Trichloroethane, Methylchloroform, Methylchloroform, Ethylidyne trichloride, Methyl chloroform, Ethylidyne chlorode, α-Trichloroethane, MC, Aliphatic halogenated derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:71-55-6
MDL number:MFCD00000806
EINECS number:200-709-7
RTECS number:KJ2975000
BRN number:None
PubChem number:24845355
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid[1]
2. Melting point (℃): -32.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 74.1[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.3376 (20℃)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 4.6[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 13.33 ( 20℃)[6]
7. Critical temperature (℃): 311.5[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.48[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.49[9]
10 .Ignition temperature (℃): 500~537[10]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 12.5[11]
12. Lower explosion limit (%): 7.5[12]
13. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, acetone, benzene, methanol , chloroform, etc. [13]
14. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 0.903
15. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 32.198
16. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 4.500
17. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): 138.1
18. Specific heat capacity ( KJ/(kg·K), -15~26ºC, average): 1.0684
19. Conductivity (S/m): 7.3×10-9
20. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.3299
21. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.4313
22. Eccentricity factor: 0.216
23. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 17.301
24.van van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 7.580×109
25. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 53.720
26. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -142.3
27. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 320.14
28. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -76.1
29. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 92.34
30. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): – 177.40
31. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 226.7
32. Liquid phase standard free energy of formation (kJ��mol-1): -83.47
33. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1):144.4
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[14]
LD50: 9600mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50 : 17000ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation[15]
Rabbit transdermal: 20mg (24h), moderate stimulation.
Rabbit eye: 100mg, mild irritation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [16] Guinea pigs inhaled 5.46g/m3, 3 hours a day, 3 Months later, liver weight increased, fatty degeneration occurred, and pneumonia occurred.
4. Mutagenicity [17] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 10μg/dish. DNA repair: E. coli 500mg/L. Gene transformation and mitotic recombination: Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5350mg/L. Cytogenetic analysis: Hamster ovary 160mg/L.
5. Teratogenicity [18] The lowest toxic dose (TDLo) of 43mg/kg was administered orally to rats from 1 to 22 days after pregnancy, causing Developmental abnormalities of the cardiovascular system.
6. Carcinogenicity [19] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G3, insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity to humans and animals.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[20]
LC50: 42.3~105mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow); 73mg/L (48h) (Medaka)
2. Biodegradability[21]
Aerobic biodegradation (h) : 3360~6552
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 13440~26208
Biodegradation-secondary sedimentation treatment (h): 220~250
3. Non-biodegradability[22]
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 5393~53929
一 Grade hydrolysis half-life (h): 0.73
4. Other harmful effects [23] This substance is harmful to the environment, special attention should be paid to groundwater pollute.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 25.82
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 95.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 222.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 28.9
5. Dielectric constant: None available
6. Polarizability ( 10-24cm3): 10.23
7. Single isotope mass: 131.930033 Da
8. Nominal mass: 132 Da
9. Average mass: 133.4042 Da
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 2.4
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 26.4
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. In the presence of cobalt, nickel, platinum, palladium salts and their oxides, the reaction can be carried out at about 150°C. In the presence of sulfuric acid or metal chloride, it is heated to 75~160°C with water under pressure to generate acetyl chloride and acetic acid. Chlorination under light gives 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane. 1,1,1-Trichloroethane without stabilizer is oxidized in high-temperature air to form phosgene. 1,1,1-Trichloroethane is very stable to milk of lime and hardly decomposes when heated to reflux.
2. Stability[24] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[25] Strong oxidants, aluminum and its alloys, strong alkali
4. Conditions to avoid contact[26] Light
5. Polymerization hazard[27] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[28] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[29] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Ethane chlorination method is produced by chlorination of ethane (or ethylene).
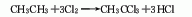
2. Vinylidene chloride hydrogen The chlorination method is obtained by the catalytic addition of vinylidene chloride and hydrogen chloride.

3. Hydrochlorination of vinyl chloride The method is to produce vinylidene chloride through the reaction of vinyl chloride and hydrogen chloride, which is then obtained by chlorination.

Purpose
1. Non-flammable solvent can be used as a cleaning agent to clean electronic parts and metal degreasing. The low surface tension and high penetration ability of this product can also be used to measure leakage at metal welds. It can also be used as an aerosol aerosol agent, flame-resistant coating material, cutting oil coolant and to make low-toxic and non-flammable adhesives. agent. Derivatives of trichloroethane are effective pesticides and intermediates in the pharmaceutical industry. 1,1,1,2-tetrachloroethane can be produced by chlorination. Vinylidene chloride can be produced by dehydrochlorination. Mainly used as solvent in the synthesis of chlorinated polyether thermoplastic polymers. Detergents, adhesives, metal cutting additives for machinery and electronic parts, etc.
2. Used as solvent and metal cleaner. [30]
�� Characteristics of high penetrating ability to determine leakage at metal welds. It can also be used as an aerosol aerosol agent, flame-resistant coating material, cutting oil coolant and to make low-toxic and non-flammable adhesives. Derivatives of trichloroethane are effective pesticides and intermediates in the pharmaceutical industry. 1,1,1,2-tetrachloroethane can be produced by chlorination. Vinylidene chloride can be produced by dehydrochlorination. Mainly used as solvent in the synthesis of chlorinated polyether thermoplastic polymers. Detergents, adhesives, metal cutting additives for machinery and electronic parts, etc.
2. Used as solvent and metal cleaner. [30]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

