Background and overview[1]
4-(Aminomethyl)benzene-1-sulfonic acid can be used as a pharmaceutical synthesis intermediate.
Preparation[1-2]
4-(Aminomethyl)benzene-1-sulfonic acid is prepared as follows:
Method 1: Add 10ml benzylamine dropwise to 30ml 20% fuming H2SO4 at 0°C with stirring. The mixture was warmed to room temperature and stirred for 30 minutes, then to 80°C for 1 hour. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction mixture was poured into 400 ml of cold dioxane. The solid formed was collected by filtration through a sintered glass funnel and washed with 50 ml of cold dioxane. The compound was purified by dissolving in a minimum volume of ammonia solution and then precipitating until pH 1 before adding concentrated HCl to give 5.5 g of the product 4-(aminomethyl)benzene-1-sulfonic acid. NMR (DMSO-d6): δ8.11 (br, s, 3H), 7.63 (d, 2H), 7.38 (d, 2H, 4.02 (s, 2H).
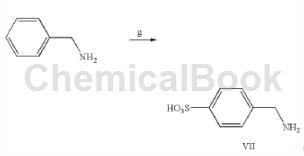
Method 2: In 535.8 parts of 5% oleum (adjusted with 401.9 parts of 96% sulfuric acid and 133.9 parts of 31.9% oleum) while maintaining the liquid temperature at 40°C or lower, 107.1 parts of benzylamine were added dropwise within one hour. After the dropwise addition, the temperature was raised to 120°C, and the reaction was carried out at the same temperature for 1 hour. After the reaction is completed, the reaction mixture is cooled to 30°C, slowly poured into 500 parts of ice water, the precipitated crystals are separated by filtration, and washed with 200 parts of cold water and 150 parts of methanol to obtain 116.2 parts of white wet cake. The obtained wet cake was dried at 80° C. to obtain 57.8 parts of 4-(aminomethyl)benzene-1-sulfonic acid.
Application
4-(Aminomethyl)benzene-1-sulfonic acid can be used as a pharmaceutical synthesis intermediate. For example, prepare the following compounds:
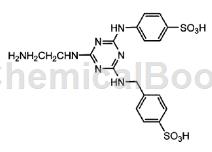
Add 18.4 parts of cyanuric chloride and Leocol TD-50 (0.05 parts) to 100 parts of ice water, and stir the mixture below 10°C for 30 minutes. Next, 19.5 parts of 4-sulfobenzoic acid was added, and the mixture was allowed to react at 0 to 10° C. for 2 hours and at 25 to 30° C. for 1 hour while adjusting the pH to 2.0 to 2.0 with a 10% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution. 2.5. Next, 21.0 parts of 4-(aminomethyl)benzene-1-sulfonic acid was added to the reaction solution, and the reaction was carried out overnight at 25 to 30°C while adjusting the pH value to 7.0 to 8.0 and perform reactions involving secondary condensates. The reaction solution containing the secondary condensate obtained as described above was gradually added to the aqueous solution obtained by adding 60.1 parts of ethylenediamine to 120 parts of ice, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. 150 parts of ice and 210 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid were added to the solution to adjust the pH to 1.0. The amount of liquid at this time is 830 parts. 190 parts of sodium chloride was added to the reaction solution, and the mixture was stirred overnight to precipitate a solid. The precipitated solid was separated by filtration to obtain 70.4 parts of wet cake. The wet cake obtained was added to 550 parts of water and dissolved with 10% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution at pH 9.0. The amount of liquid at this time is 630 parts. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 1.0 with concentrated hydrochloric acid, 140 parts of sodium chloride was added, and the mixture was stirred overnight to precipitate a solid. The precipitated solid was separated by filtration to obtain 27.2 parts of wet cake. The obtained wet cake was added to a mixed solvent of 255 parts of methanol and 45 parts of water, stirred at 50° C. for 1 hour, and the precipitated solid was separated by filtration, thereby obtaining 42.2 parts of wet cake. The obtained wet cake was dried to obtain the desired white powder, which was 16.3 parts of the sodium salt of the compound represented by formula (109).
Main reference materials
[1] (US20080124807)Proteintaggingreagents
[2] (JP2011184575) AQUEOUS INK COMPOSITION, INKJET RECORDING METHOD AND COLORED OBJECT

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

