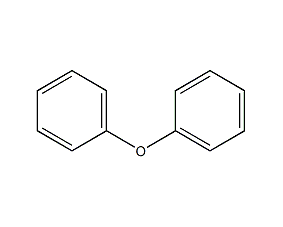
Structural formula
| Business number | 02L7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C12H10O |
| Molecular weight | 170.21 |
| label |
phenyl ether, biphenyl oxide, Diphenyl oxide, Phenyl ether, Biphenyloxide, heat carrier, soap spices, Defoaming agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:101-84-8
MDL number:MFCD00003034
EINECS number:202-981-2
RTECS number:KN8970000
BRN number:1364620
PubChem number:24854438
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless crystals, which turn into light yellow oily liquid when heated above the melting point, with a special odor.
2. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4ºC, liquid): 1.0748
3. Relative density (g/mL, 20/20ºC): 1.0863
4. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 5.86
5. Melting point (ºC): 28
6. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa) : 257.9
7. Refractive index (n20D): 1.5780
8. Flash point (ºC): 111
9. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 3.864
10. Fire point (ºC): 620
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 20ºC): <1
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 66.1ºC): 0.13
13. Critical temperature (ºC): 493.85
14. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): 1.5
15. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): 0.8
16. Solubility: insoluble in Water, soluble in alcohol, ether, benzene, glacial acetic acid, etc. Insoluble in concentrated sulfuric acid.
17. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.0712
18. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.569245
19. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.578725
20. Critical density (g· cm-3): 0.322
21. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 529 p>
22. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 18.774
23. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 1.126×1010
24. van der Waals volume (cm3 ·mol-1): 95.380
25. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): – 6203.28
26. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -52.01
27. Liquid phase standard heat of combustion (enthalpy) )(kJ·mol-1): -6136.38
28. The liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -14.90
29. Crystalline phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -6119.2
30. Crystalline phase standard claim Heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -32.1
31. Crystal phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 233.91
32. Crystal phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1· K-1):216.56
Toxicological data
LD/LC50 amounts related to classification:
Oral LD50 2450mg/kg(rat)
Skin LD50 >7940 mg/kg(rat)
Skin irritation mild 500mg/24h(rbt)
Main irritating effects:
On the skin: May cause inflammation.
On eyes: May cause irritation.
Sensitization: No known sensitizing effects.
Ecological data
General remarks
Ecotoxicity effects
Remarks: Toxic to fish
Water hazard class 2 (German regulations) (self-assessment via list) The Substances and their hazards to water.
Do not allow this product to come into contact with groundwater, waterways, or sewage systems, even in small amounts.
Even extremely small amounts of product seeping into the ground can pose a hazard to drinking water.
It is also poisonous to fish and plankton in water bodies.
Do not discharge materials into the surrounding environment without government permission.
Highly toxic to organic matter in water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 52.69
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 160.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 398.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 38.4
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 20.89
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 9.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 116
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants. Is a flammable substance. Pay attention to the source of fire and use foam fire extinguishing agent, carbon dioxide or dry fire extinguishing agent to extinguish the fire. It is of low toxicity.
Chemical properties: It is relatively stable in aqueous solutions of amines or alkalis. When heated, the ether bond is easily broken and decomposed into phenol. For example, when diphenyl ether is heated and refluxed with metallic sodium or potassium in pyridine, more than 90% of it becomes phenol. Grignard’s reagent can also break ether bonds. When anhydrous cobalt chloride is used as a catalyst, the reaction can proceed at room temperature. It does not decompose when heated to 250°C with hydrogen iodide. It is also relatively stable to chromium oxide (CrO3, Cr2O3) in acetic acid. When diphenyl ether reacts with concentrated nitric acid, 4,4′-dinitrodiphenyl ether is generated.
2.Low toxicity. The maximum allowable concentration in the air in the workplace is 1×10-6. Packed in iron drums, 200kg per drum.
3. Found in oriental tobacco leaves.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. 2. Equip with corresponding varieties and quantities of fire-fighting equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials. 3. Store and transport according to the regulations on toxic substances.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the condensation of chlorobenzene and phenol in caustic alkali solution using copper as catalyst. Mix potassium hydroxide, phenol and chlorobenzene in a molar ratio of 1:1.4:1.06, add copper powder, stir and heat to perform a condensation reaction. After the reaction is completed, it is treated with acid to separate the diphenyl ether oil layer and distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the finished diphenyl ether product. Chlorobenzene and phenol can also be reacted in sodium hydroxide solution. Another industrial source of diphenyl ether is as a by-product of the hydrolysis of chlorobenzene to phenol. During the hydrolysis of chlorobenzene with sodium hydroxide, about 10% of the chlorobenzene is converted into diphenyl ether, and in some processes this proportion can reach 20%. The diphenyl ether product is obtained through extraction and refining.
Refining method: wash with sodium hydroxide solution and water, dry with calcium chloride and fractionate under reduced pressure. Aldehyde impurities can be removed by p-nitrophenylhydrazine precipitation.
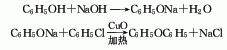
2. Tobacco: OR, 26 ;OR,18.
Purpose
1. Substitute for low-grade geranium oil. Suitable for preparing floral cosmetics, soap essences and deodorants.
2. It can be used in the engineering plastics pharmaceutical industry and as heat carrier and heat transfer medium, and is temporarily used as edible spices. In addition, it is also used as fragrance and defoaming agent in soap.
3. Used in daily fragrance formulas and in the preparation of artificial geranium oil. Because the aroma of diphenyl ether is relatively rough, a large amount of diphenyl ether is mainly used in low-end soap fragrances, synthetic detergent fragrances and other daily chemical product fragrance formulas.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

