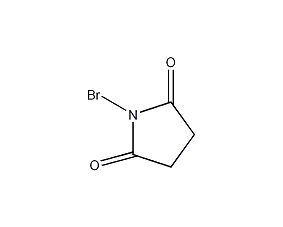
Structural formula
| Business number | 03LD |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H4BrNO2 |
| Molecular weight | 177.99 |
| label |
N-bromosuccinimide, N-Succinbromimide, 1-Bromo-2,5-pyrrolidine-dione, NBC |
Numbering system
CAS number:128-08-5
MDL number:MFCD00005510
EINECS number:204-877-2
RTECS number:None
BRN number:None
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Appearance: white powder or crystal
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 2.097
3. Melting point (ºC, microdecomposition): 173~175
4. Solubility: Easily soluble in acetone, ethyl acetate, acetic anhydride, insoluble in water, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, chloroform, etc.
Toxicological data
None
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 30.06
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 87.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 250.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 67.8
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.91
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 3
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 37.4
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 129
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. This product is highly toxic. Strongly irritating to eyes, mucous membranes and skin. The workshop should be well ventilated.
2. Production equipment should be sealed to prevent leakage, and operators should wear protective equipment.
3. Sensitive to moisture and should be stored in the refrigerator. During use, avoid inhalation or sticking to the skin, and generally operate in a fume hood with good ventilation.
4. It has a strong hot and irritating smell and is highly irritating to the eyes, skin and mucous membranes.
Storage method
Synthesis method
1. Dissolve succinimide (succinimide) in 10 times the mass of water, decolorize, filter and clear, then add bromine water with the same mass as succinimide dropwise at 15°C while dripping Add 20% sodium hydroxide solution and control the pH of the solution = 7 to 8. White crystals will precipitate during the dropwise addition. After the addition, continue stirring for half an hour, let it stand, filter, wash the crystals with distilled water several times until the bromine and succinimide content is acceptable, spin dry, and dry to obtain the finished product.
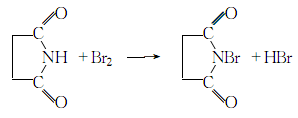
2. Dissolve 160 g (1.62 mol) succinimide in a mixture of 64 g (1.60 mol) sodium hydroxide, 300 g crushed ice and 400 ml water. While hot, stir and cool, add 85 ml at a time (carefully). Continue stirring for 1 to 2 minutes and filter out the precipitate. Wash the crude product with ice water to remove the remaining odor, then place it in a phosphorus pentoxide dryer and dry it for 8 hours under a pressure of 0.5 mmHg; or place it in a drying gun (phosphorus pentoxide) at 40°C After drying for 8 hours under a pressure of 10-20mm mercury, 220-230 grams (75-51%) of product with a purity of approximately 97% was obtained.
Purpose
1. Organic synthetic raw materials, used to regulate low-energy bromination reactions, and also used to produce rubber additives and pharmaceuticals. Can synthesize bromoacetonitrile medicine. It is used in the pesticide industry to synthesize thiabendazole, and can also be used as a fruit preservative, antiseptic, and antifungal agent.
2. Used for photometric determination of quercetin coexisting with other flavonoids. Also used in organic synthesis.
3. Brominating agent. Alkenes are converted into anti-Markownikoff law products. oxidizing agent. After the aldehyde is oxidized to acid bromide, it can be further reacted to obtain acetate and acid amine. Oxidation of allyl groups is often better than chromium trioxide-pyridine. It is often used together with dimethylformamide or dimethyl sulfoxide as a more effective brominating agent.
4.N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS) is often used in the free radical bromination reaction of allyl and benzyl groups[1]; Electrophilic bromination of ketones, aromatic compounds or heterocyclic compounds; Hydroxylation of alkenes, ether-forming reactions and lactonization reactions.
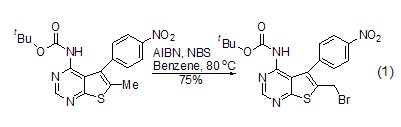
Free radical bromination reaction Under appropriate conditions, NBS can efficiently react with allyl compounds in free radical bromination reactions, and the reaction is highly selective. (Formula 1)[1].
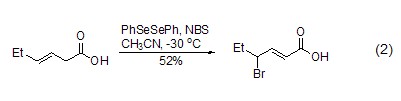
Unsaturated carboxylic acids, aldehydes, esters and lactone compounds can also be brominated using NBS. During the bromination process of unsaturated carboxylic acids, the unsaturated bonds may migrate to generate α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid (formula 2)[2].
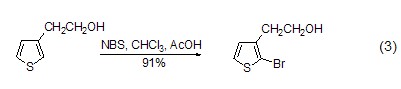
Electrophilic bromination reaction Under the action of NBS, phenol, aniline and other electron clouds Aromatic compounds with higher density can efficiently generate ortho- or para-brominated products (formula 3)[3~5].
Reaction with vinyl or alkynyl compounds In the presence of organometallic compounds, NBS can convert alkyne and other compounds into the corresponding bromide (Formula 4 )[6].
Addition with carbon-carbon double bonds Under the action of other nucleophiles, NBS can undergo addition reactions with compounds such as alkenes (Formula 5)[ 7], nucleophiles include alcohols, carboxyl groups, azide compounds, sodium alkoxides, etc. Through addition reaction, a variety of functional groups can be introduced into the product. This method is a relatively common method in the synthesis of natural products[8~11]. 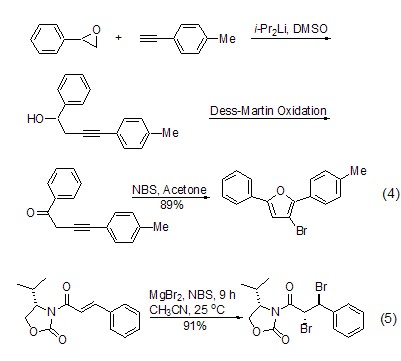
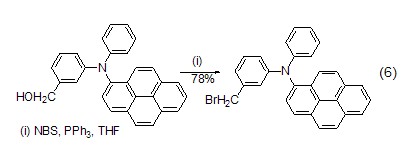
Brination reactions of other functional groups in In polar solvents, NBS can convert primary or secondary alcohols into the corresponding bromide (formula 6) in the presence of PPh3.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

