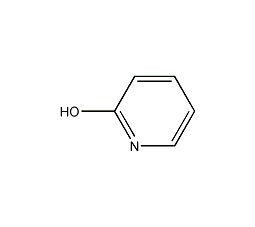
Structural formula
| Business number | 03UQ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H5NO |
| Molecular weight | 95.10 |
| label |
2-pyridinol, 2-pyridone, 2-Pyridinol, 2-Pyridone, ampholytic nucleophile |
Numbering system
CAS number:142-08-5
MDL number:MFCD00006268
EINECS number:205-520-3
RTECS number:UV1144050
BRN number:105786
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: white or brown crystalline powder
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.391
3. Flash point (℃): 210
4. Melting point (℃): 104-109
5. Boiling point (ºC): 280-281
6. Relative density: 1.39
p>
7. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): 0.0003
8. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): -2516
9. Solubility: soluble in H 2O, EtOH, CHCl3, partially soluble in Et2O, C6H6 , almost insoluble in light petroleum and hexane.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: mouse abdominal LD50: 410 mg/kg; mouse intravenous LD50: 750 mg/kg.
Ecological data
Other harmful effects: This substance may be harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 26.22
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 81.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 216.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 50.7
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.39
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 29.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 135
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Storage method
Frozen storage is better under inert gas.
Synthesis method
Reflux at 181~185 oC/24 mmHg to remove colored impurities, and then reflux in EtOH, CHCl3/diethyl ether, C6H6, C6H6/hexane or CCl4 ; Pure product can be obtained through continuous recrystallization or sublimation, or a combination of both.
Purpose
2-Pyridone is an amphiphilic nucleophile [1], which can undergo [4+2] cycloaddition [2] as a diene. Often used in peptide synthesis to form active esters[3]. 2-Pyridone is the classic tautomerization substrate of iminoalcohol and amide (formula 1)[4].
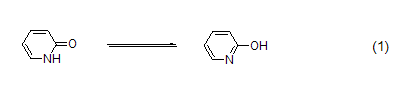
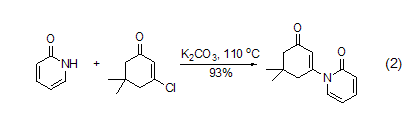
In polar solvents, the The compound is more likely to exist in the pyridone form; as the solvent becomes less polar, an equilibrium between hydroxypyridine and pyridone occurs. In the gas phase, it mainly exists in the form of hydroxypyridine. Therefore, nucleophilic substitution reactions tend to produce mixtures. In a simple alkylation reaction, if the conjugate base 2-pyridone is used as a nucleophile, anN-alkylation product will be formed. For example, in the presence of potassium carbonate, 2-pyridone is added to 3-chloro-5,5-dimethyl-2-cyclohexanone to obtain a conjugate addition-elimination product (formula 2)[5].
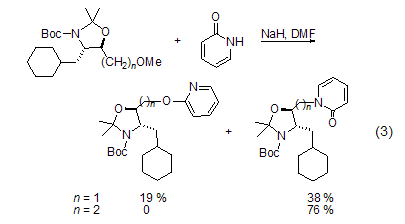
Under the catalysis of Pt or Pd, you can Perform stereoselectiveN-alkylation. The effects of solvents and counterions affect the reaction: N-alkylation is prone to occur in polar solvents; while O is prone to occur when the Ag salt of 2-pyridone is present. -Alkylation[2]. In the presence of triethylamine, trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate is used as the electrophile to obtain silicon ethers. Likewise, 2-pyridone reacts with chlorodimethylphosphine to give dimethylphosphine as a single product. The methylation reaction of 2-pyridone and diazomethane is kinetically controlled, and the ratio of the obtained N-methyl product to the O-methyl product is 60 :40; however, the only O-methylated product is obtained when reacting with a strong electrophile. In addition, the structure of the substrate will also affect the regioselectivity of alkylation (Formula 3)[6].
2-pyridone at low temperature Acetylation often results in a mixture; as the temperature gradually returns to room temperature, the N-acetylated product will gradually transform into the more thermodynamically stable O-acetylated isomer ( Formula 4)[7]. Benzoylation and trifluoromethylsulfonylation of 2-pyridones occur only on oxygen. 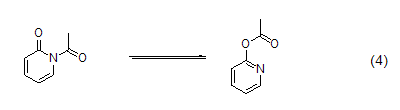
The [4+2] cycloaddition of 2-pyridones is usually It’s hard to happen[3]. Because 2-pyridone is more prone to conjugate addition with dienophiles, but N-alkyl derivatives, especially N-methyl and N-alkenyl derivatives react with highly reactive dienophiles such as dimethyl butynedioate, maleic anhydride or benzyne at high temperature or pressure to form isoquinine addition Object (Formula 5)[8]. Under heating conditions, these adducts can remove isocyanates to give aromatization products. The related N-phenylsulfonyl-3-(p-sulfonylbenzyl)-2-pyridone can undergo an electron-deficient Diels-Alder reaction with the dienophile allyl ether. These ring-forming reactions proceed more easily under high-pressure conditions.
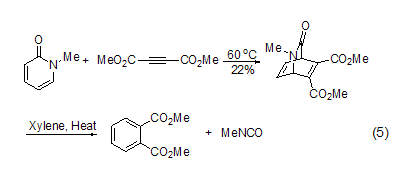
AlthoughN-(ω-alkenyl)-2-pyridone is difficult to occur, but the [2+2] cycloaddition of some light-sensitive molecules Addition is a good method for the synthesis of stereochemically defined tricyclic lactones. An example is the specific 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of DMAD with methyleneamine ylide to obtain indole compounds [9].
2-Pyridone can be used for the preparation of “active esters” in solid-phase peptide synthesis[3]. If the synthesis of the peptide is carried out in methylene chloride, these esters are more reactive than the corresponding p-nitrophenyl esters. In the reaction to prepare 2,2,2-trichloroethyl ester of amino acids, 2-pyridine ester participates in the reaction as an intermediate (Formula 6)[10].
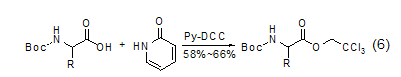
2-pyridone can also be used as Ligands of metal compounds participate in the reaction[11].

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

