Overview[1]
O-fluorobenzene is mainly used as an intermediate for medicines and pesticides. It is a chemical substance composed of a variety of chemical raw materials that is harmful if swallowed and irritates the eyes, respiratory system and skin. The existing production of o-fluorobenzene generally uses external Protection, no effective measures have been taken for exhaust gas emissions. Therefore, it has become a problem for us to provide a distillation tower for the production of o-fluorobromobenzene that can solve the problems of exhaust gas emissions, complex structure and dangerous problems in the production process.
Structure
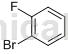
Apply[2-5]
O-fluorobenzene is mainly used as a pharmaceutical and pesticide intermediate. Examples of its applications are as follows:
1) Preparation of o-fluorobenzene cyanide. Put cuprous cyanide, o-fluorobenzene, and DMF into the reaction bottle in sequence. Heating to reflux at 128-160°C, the material liquid changed from light gray-green turbidity to brown turbidity. Keep time for 8-9 hours. During the heat preservation process, the temperature gradually rises. In the last 3 hours, the temperature is 180℃±2., the material liquid is brown and turbid, and the reaction is stopped. Cool to room temperature, add water, and steam distillation. Control the water volume and stirring speed to prevent Later distillation and punching ensure complete distillation. The oil layer is separated to obtain o-fluorobenzene cyanide, GC99%, individual impurities are less than 0.5%, and the yield is 90%.
2) Preparing o-fluorobenzaldehyde, including the following steps: dissolve propyl formate in anhydrous tetrahydrofuran to obtain solution A; dissolve o-fluorobenzaldehyde in anhydrous tetrahydrofuran to obtain solution B; dissolve anhydrous lithium chloride and magnesium into the reaction flask, add anhydrous tetrahydrofuran, heat to slightly boiling, add dibromoethane dropwise to initiate the reaction; under reflux, add solution B into the reaction flask; after the feeding is completed, cool down, and then add solution A dropwise; the feeding is completed , continue the reaction for a period of time; cool down, quench with dilute hydrochloric acid, post-process, and purify under vacuum distillation to obtain 1?phenyl?2?butanone. In the method of the present invention, when preparing the Grignard reagent, lithium chloride is added to form a stable and relatively low-activity benzyl magnesium lithium chloride; propyl formate reacts with it in a controllable manner and only reacts with a relatively low-activity benzyl magnesium lithium chloride. The reaction stays at the aldehyde stage rather than proceeding to the alcohol stage.
3) Preparation of 3-chloro-7(5)-bromobenzisoxazole, using o-fluorobromobenzene as raw material, acidification to obtain 2-fluoro-3-bromobenzoic acid, and then 2-fluoro- After esterification of 3-bromobenzoic acid, 2-fluoro-3-bromobenzoic acid methyl ester is obtained, and then 2-fluoro-3-bromobenzoic acid methyl ester is reacted with N-acetylhydroxylamine to obtain 7-bromo-3-bromobenzoic acid. Benzisoxazole, finally chlorine 7-bromo-3-benzisoxazole to obtain 3-chloro-7-bromobenzisoxazole; use 2-fluoro-5-bromobenzoic acid as raw material, After esterification of 2-fluoro-5-bromobenzoic acid, 2-fluoro-5-bromobenzoic acid methyl ester is obtained, and then 2-fluoro-5-bromobenzoic acid methyl ester is reacted with N-acetylhydroxylamine to obtain 5- Bromo-3-benzisoxazolone, and finally chlorination of 5-bromo-3-benzisoxazolone gives 3-chloro-5-bromobenzisoxazole. The invention has low raw material prices, low cost, few reaction steps, simple post-processing, high overall yield, and can reduce environmental pollution.
4) Preparation of 1-R-1”-spiro-(piperidine-4,4”-quinoline)-2”(3”-hydro)onesine.
Solve the technical problem that existing synthesis methods are not rich enough. The preparation includes the following steps: using 1-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-4-piperidone as a raw material, in a solvent, adding a condensation catalyst and ethyl cyanoacetate for reflux reaction, and obtaining 4-((ethoxycarbonylcyano) after purification )Methylene)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 1; Compound 1 reacts with isopropyl Grignard reagent and o-fluorobenzene under the catalysis of metal halide to obtain 4-((ethoxycarbonylcyano)methyl base)-4”-((2-fluoro)phenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 2, compound 2 is hydrolyzed under alkaline reagent conditions to obtain 4-((carboxycyano)methyl)- 4”-((2-fluoro)phenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 3; compound 3 is decarboxylated with cuprous oxide or copper powder in acetonitrile solvent to obtain 4-(ethylcyano)-4 ”-((2-fluoro)phenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 4; Compound 4 is then hydrolyzed with hydrogen peroxide/alkaline reagent to obtain 4-(acetamido)-4”-(( 2-Fluoro)phenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 5; compound 5 is cyclized with an alkaline reagent/DMF system in a solvent to obtain the target product.
Preparation[2]
The reaction flask was put into o-fluoroaniline and hydrobromic acid in turn and stirred. A large amount of purplish red solid precipitated out of heat. The maximum temperature was 60°C. After stirring for 5 minutes, add sodium nitrite solution dropwise in an ice-salt bath below -10°C. The heating process releases heat�The material liquid gradually turns orange and clear, and the dripping is completed in about 40 minutes. After the dripping is completed, keep it warm for 10 minutes, add urea, cool it, and put copper bromide, hydrobromic acid, water, and oil bath into the reaction bottle with distillation device. Raise the temperature to 120-130°C and pass water vapor. When the internal temperature is about 105°C, water vapor will evaporate. Begin to drip the diazonium salt. At this time, a large number of bubbles will be generated. Control the dripping speed to maintain the distillation state to ensure that the generated o-fluorobromobenzene is produced. Quickly carried away by water vapor. It takes about 50 minutes to finish dripping, then steam for another 5 minutes to stop distillation. Separate the oil layer and wash it with saturated brine. After filtering, the moisture content of the oil layer is measured to be 0.04% to obtain o-fluorobenzene.
Main reference materials
[1] CN201821092029.7 A distillation tower for producing o-fluorobenzene
[2] CN200810139124.2 Preparation method of o-fluorobenzene cyanide
[3] CN201910033467.9 A preparation method of o-fluorobenzaldehyde
[4] CN201310341708.9 A synthesis method of 3-chloro-7(5)-bromobenzisoxazole
[5] CN201010568585.9 A preparation method of 1-R-1’-spiro-(piperidine-4,4’-quinoline)-2’(3’-hydro)one

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

