Background and Overview
α-Bromo-2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorotoluene is a benzene derivative that can be used as a derivatization reagent for gas chromatography analysis of multifunctional thiols, and can also be used to prepare pentafluorobenzene ester.
Apply[1]
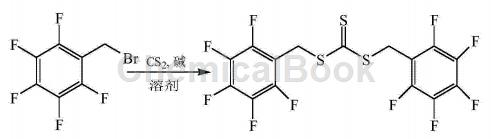
α-Bromo-2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorotoluene can be used to prepare trithiocarbonate-bis(pentafluorobenzyl)ester:
Reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT polymerization) is a typical controllable and living radical polymerization method. In recent years, RAFT polymerization has become an important method for the design and synthesis of polymer molecules due to its wide application range of monomers, mild polymerization conditions, and ability to effectively control the product structure. As well as the synthesis of polymers with complex topological structures such as stars, it has been widely studied and applied. Practice has shown that the key factor in realizing RAFT polymerization is the design and selection of a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer agent (i.e., RAFT reagent) suitable for the target monomer.
The RAFT reagents currently used are mainly some trithiocarbonates, dithiocarboxylates, dithiocarbamates and xanthate esters. These RAFT reagents are mostly used for some fluorine-free monomers ( Such as the polymerization system of styrene, (meth)acrylic acid, (meth)acrylate and some vinyl ether monomers), the products prepared are mostly fluorine-free polymers.
CN201410497677.0 overcomes the shortcomings of existing RAFT reagents such as difficulty in effectively controlling the polymerization process of high fluorine-containing monomers and the unstable end groups of the resulting polymerization products, and provides a method with excellent solubility and energy in supercritical carbon dioxide. Fluorine-containing RAFT reagents that effectively control the polymerization process of fluorine-containing monomers and can provide highly stable fluorine-containing end groups for polymers. The synthesis process is as follows: Dissolve carbon disulfide in the solvent, then add α-bromo-2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorotoluene dropwise, stir thoroughly, add alkali, α-bromo-2,3,4, The molar ratio of 5,6-pentafluorotoluene, carbon disulfide, alkali and solvent is 1:1~3:0.5~2:10~40. Stir at 25~50°C for 12~24 hours. Add ice water to quench the reaction. The product is separated and purified to obtain trithiocarbonate-bis(pentafluorobenzyl)ester. The molar ratio of α-bromo-2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorotoluene, carbon disulfide, and alkali is preferably 1:2 to 2.5:1 to 1.5.
The preparation process of trithiocarbonate-bis(pentafluorobenzyl)ester of the present invention is simple to operate. The fluorine-containing acrylate polymer synthesized as a RAFT reagent has high fluorine-containing end groups. In addition to good hydrophobicity, the polymer In addition to its stain resistance, high fluorine-containing end groups are expected to improve its thermal stability and light transmittance, thereby meeting the application requirements of polymer materials under special conditions. In addition, fluorine-containing acrylate monomers and their polymers with high fluorine content have good solubility in supercritical carbon dioxide. Therefore, the trithiocarbonate-di(pentafluorobenzyl) ester and fluorine-containing acrylic acid of the present invention are used Ester monomers are expected to achieve homogeneous RAFT polymerization under milder pressure conditions in supercritical carbon dioxide systems.
Main reference materials
[1] CN201410497677.0 Trithiocarbonate-bis(pentafluorobenzyl)ester and its preparation method and application

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

