Background and overview[1]
2-Amino-4-bromobenzaldehyde can be used as a pharmaceutical synthesis intermediate, which can be prepared by reaction with 2-amino-4-bromobenzoic acid as the starting material. 2-Amino-4-bromobenzaldehyde can be used to prepare ethyl 3-amino-7-bromoquinoline-2-carboxylate. Most heterocyclic compounds have certain biological activity, and quinoline compounds are a type of heterocyclic compounds with both biological and pharmacological activities. Among them, aminoquinoline is an important quinoline derivative with high biological activity.
Preparation[1]
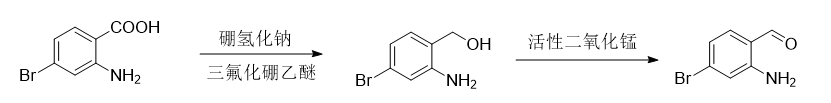
Step 1: Synthesis of 2-amino-4-bromobenzyl alcohol
Add 60g NaBH4 into 300mL tetrahydrofuran (THF) and stir mechanically. Under an ice-water bath, add 100g of 2-amino-4-bromobenzoic acid to the solution, then add dropwise 27mL of boron trifluoride ether solution, and control the temperature below 20 degrees. After the dropwise addition is completed, the reaction solution is raised to room temperature and allowed to react overnight until the raw materials are completely reacted. Add 300 ml of MeOH dropwise to the reaction solution. After the addition is complete, add 5N NaOH (200 ml) and stir for about half an hour. The organic solvent in the reaction solution was spin-dried and cooled to room temperature. The solid was precipitated and filtered to obtain about 60 g of crude 2-amino-4-bromobenzyl alcohol [mass spectrometry (MS) M+1 203]. The yield is 98.7%.
Step 2: Synthesis of 2-amino-4-bromobenzaldehyde
Add 60g of the product obtained in step 1 and 300g of manganese dioxide into 1L of methylene chloride solvent, stir mechanically, and react overnight. Pass the reaction solution through diatomaceous earth and pass through a column (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 5:1) to obtain about 40g of 2-amino-4-bromobenzaldehyde [H NMR spectrum (400MHz, CDCl3): δ6.72-6.75(d, 1H), 7.23(bs, 2H), 7.38-7.42(dd, H), 7.72-7.73(d, 1H), 9.77(s, 1H)]. The yield is 85.2%.
Apply[1]

2-Amino-4-bromobenzaldehyde can be used to prepare ethyl 3-amino-7-bromoquinoline-2-carboxylate: Dissolve 40.8 g of ethyl bromopyruvate in 192 ml of ethanol at room temperature , and then slowly drop into a mixture of 16 grams of pyridine and 200 ml of ethanol for more than 30 minutes to ensure complete reaction. After raising the temperature to 60 degrees and reacting for 1 hour, it was cooled to room temperature. Add 40 grams of 2-amino-4-bromobenzaldehyde, then add 32 ml of pyridine, reflux for 4.5 hours, then add 34.1 grams of pyrrolidine, and reflux for 3 hours to close the amino group on the ring. After the TLC detection reaction (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 5:1) is completed, spin off most of the ethanol, add water and ethyl acetate for extraction. Pass through the column (petroleum ether:ethyl acetate=5:1). Spin dry to obtain 19 g of ethyl 3-amino-7-bromoquinoline-2-carboxylate. [Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum 400MHz, CDCl3): δ1.50-1.53(t, 3H), 4.53-4.59(q, 2H), 7.35(s, H), 7.44-7.46(d , 1H), 7.52-7.54(dd, 1H), 8.29-8.30(m, 1H)]. The yield is 72.3%.
References
[1] CN201210433925.6 3-Amino-7-bromoquinoline-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester and its preparation method

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

