Background and overview[1-3]
Tantalum reagent is also called N-benzoylphenylhydroxylamine, which can be prepared by acylation of phenylhydraline and benzoyl chloride. In analysis, tantalum reagent (BPHA) extraction photometry is commonly used to determine the content of vanadium.
Preparation[1]
The tantalum reagent is compound 2 in the picture below.
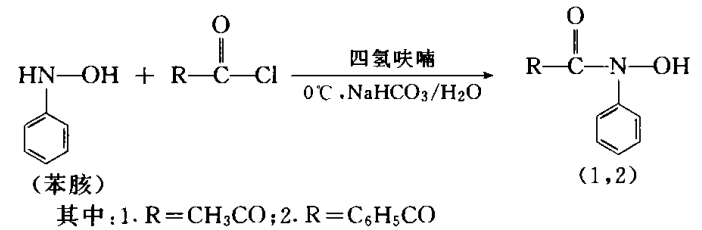
In a 500mL three-neck round-bottomed flask, add 18g phenyhydrone and 100mL tetrahydrofuran (pre-cooled to 0°C), as well as a paste of 30g sodium bicarbonate and 20mL water, and install a mechanical stirrer, thermometer and dripping solution funnel, adjust the stirring speed to make the sodium bicarbonate disperse as evenly as possible in the reaction solution. The reaction bottle was placed in an alcohol cold trap to keep the temperature of the reaction solution at 0°C. Then benzoyl chloride was added dropwise from the dropping funnel (the molar ratio of phenylhydroxylamine to acylating reagent was 1:1.05). After adding the acylating reagent, continue stirring for 20 minutes, then add 100 mL of 10% sodium hydroxide solution and 80 mL of petroleum ether to the reaction solution, and separate the sodium hydroxide solution phase and the organic phase after stratification. Wash the organic phase twice with 50 mL of 10% sodium hydroxide solution and separate the sodium hydroxide solution. Combine the above sodium hydroxide solutions, extract with dichloromethane, then use hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value of the sodium hydroxide solution to 6.0, then extract with dichloromethane three times, and concentrate the dichloromethane solution to one-fifth. Then petroleum ether is added, and after freezing, the product crystallizes out.
Apply[2-3]
Vanadium is one of the important alloying elements in steel, which can improve the strength, toughness, hardness and wear resistance of steel. The analysis of low vanadium in alloy steel is usually carried out by photometry. There are four main photometric methods for measuring vanadium: tantalum reagent (BPHA) extraction photometry, PAR [i.e. 4-(2-pyridylazo)-isophenylene di Phenol (PAR)] photometry, sodium diphenylamine sulfonate photometry and heteropolyacid photometry [1]. Among these four analysis methods, tantalum reagent (BPHA) extraction photometry is the most researched and most widely used photometric method for determining vanadium, and it is also a determination method included in the national standard. CN201010598006.5 discloses a method for the determination and analysis of V content in carbon materials. Anhydrous sodium carbonate or/and boric acid is used as a flux. After the ash after burning of the carbon materials is melted, the test is leached with dilute hydrochloric acid solution. solution, add potassium permanganate to oxidize the vanadium to pentavalent, extract the pentavalent vanadium with a chloroform solution of N-benzoyl hydride (tantalum reagent), and use colorimetric analysis to determine the V content. This patent provides a method for the determination and analysis of V content in carbon materials that is simple to operate and highly accurate.
References
[1] Fu Shiyu, Zhan Huaiyu, Yu Huisheng. Synthesis of N-acylated phenylhydroxylamine derivatives [J]. Chemical Reagents, 2000(02):118-127.
[2][Chinese invention] CN201010598006.5 A method for determination and analysis of V content in carbon materials
[3] Wei Xiaoxiang, Yu Lili. Determination of trace vanadium content in alloy steel by tantalum reagent extraction photometry [J]. Chemical Engineering and Equipment, 2010(03):148-149+109.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

