Background and overview[1]
Monobenzone is a topical depigmenting agent used to treat hyperpigmentation, such as various stains, age spots, melanoma, etc. The effect is very obvious. It can decompose melanin in the skin, prevent the production of melanin in the skin, and restore the healthy color of the skin without destroying melanocytes. It is very lightly toxic and is usually made into ointments or liniments. It has been included in the United States Pharmacopoeia and has not yet been produced in my country. . At present, there are no drugs for the treatment of spots in our country, and the cosmetics used for the treatment of spots have little effect, and some cosmetics add large amounts of harmful substances such as hydroquinone and metallic mercury to achieve the effect of removing spots and whitening. Developing monobenzone into anti-freckle medicines or cosmetics has good effects and low toxicity, which can meet the urgent needs of a large number of yellow people suffering from spots, and will be welcomed by domestic and foreign markets. The ex-factory price of each ointment (ointment or cosmetic ointment) is 80 yuan, and the cost of each tube is 12 yuan. The annual production scale is 3 million pieces, the output value reaches 240 million yuan, and the annual net profit is 120 million yuan. The total investment is about 11 million yuan, and profits can be made that year. The results of this product have been tested on the pigmented spots and age spots on the faces of trial users, showing that it is a highly efficient and low-toxic product. In addition to being developed into medicines, monobenzone can also be developed into cosmetics. It is simple to apply for approval and has quick results, so its application prospects are very good. However, as a new drug development, companies still need to invest considerable financial support to complete pharmacological and clinical trials and obtain the national new drug certificate.
Apply[2-3]
Monobenzone is a topical depigmenting agent used to treat hyperpigmentation, such as various stains, age spots, melanoma, etc. The effect is very obvious. It can decompose melanin in the skin, prevent the production of melanin in the skin, and restore the healthy color of the skin without destroying melanocytes. It is very toxic and is usually made into ointments or liniments. It has been included in the United States Pharmacopeia.
In addition, recent studies have shown that monobenzone combined with imiquimod is more effective in modeling vitiligo in C57BL6 mice than monobenzone or imiquimod alone. Thirty 4-week-old C57BL6 mice were divided into 3 groups A, B, and C. Group A was treated with 40% monobenzone combined with 5% imiquimod, group B was treated with 40% monobenzone, and group C was administered with 40% monobenzone combined with 5% imiquimod. 5% imiquimod was applied to the lower back of the mice once a day in each group for 60 consecutive days. Another 5 C57BL6 mice were selected as the negative control group without any treatment. Results: Both groups A and B showed depigmentation at the application site 2 weeks after application. There was no statistically significant difference in the time when depigmentation began between the two groups (t=1.23, P>0.05), but after 2 months, both groups showed depigmentation. Comparing the depigmentation scores of the applied parts in the group, the difference was statistically significant (t=2.43, P<0.05); the depigmentation of the non-applied parts of group A was statistically significant compared with that of group B (t=2.45, P <0.05); in group C, only 1 mouse showed a small amount of depigmentation at the application site. The negative control group showed no depigmentation and hair loss.
Monobenzone is effective in treating or preventing herpes virus infections. The CC50 of monobenzone on HONE-1 cells is 1000 μmol/L. Monobenzone can inhibit EBV lytic phase replication in a dose-dependent manner, and its IC50 for EBV lytic phase DNA replication is 0.63 micromol/L. The CC50 of monobenzone on Vero cells is 652.4 μmol/L. Monobenzone inhibits HSV-1 replication with an IC50 of 0.81 micromol/L. Monobenzone inhibits HSV-2 replication with an IC50 of 1.92 micromol/L. The CC50 of monobenzone on HFF cells is 550 μmol/L. The IC50 of monobenzone for inhibiting HCMV replication is 4.97 micromol/L.
Preparation[4]
Monobenzone was synthesized under microwave irradiation using hydroquinone, sodium hydroxide and benzyl chloride as raw materials and N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as the solvent. The single-factor experimental method was used to investigate the effects of the molar ratio of reactants, microwave radiation power and radiation time on the yield of monobenzone. The experimental results show that when n (benzyl chloride): n (hydroquinone): n (sodium hydroxide) = 1: 1.4: 1.4, DMF 15mL, microwave radiation power 320W, radiation time 60s, monobenzene The yield of the sample was 63.79%.
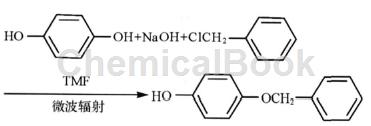
Add 2.63g (0.028mol) hydroquinone into a 100mL Erlenmeyer flask, weigh 1.12g (0.028mol) sodium hydroxide, add 8mL water, wait until the sodium hydroxide dissolves, then add dropwise until the paraben is contained Diphenol in an Erlenmeyer flask, shake well, then add 15mLDMF and 2.52g (0.02mol) benzyl chloride, and radiate the reaction for 60s under the condition of microwave radiation power of 320W. After the reaction was completed, it was cooled to room temperature. First use 10% sodium hydroxide to make it alkaline, suction filter, and wash the filter cake with 10% sodium hydroxide until the filtrate becomes colorless (the filter cake is hydroquinone bisbenzyl ether, which can be recycled). The filtrate was acidified with hydrochloric acid to completely precipitate monobenzone. After suction filtration and washing with ice water, it was recrystallized with alcohol and water and decolorized with activated carbon to obtain 2.55g of white solid with a yield of 63.79%.
Main reference materials
[1] Powerful freckle remover—monobenzone
[2] Study on the effect of monobenzone combined with imiquimod on vitiligo modeling in C57BL6 mice
[3] CN201510675321.6 Use of monobenzone in the preparation of medicines
[4] Research on the synthesis of monobenzone by microwave radiation

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

