Background and overview[1]
Etizolam is a benzodiazepine anti-anxiety drug. Its anti-anxiety effect is 3 to 5 times stronger than that of diazepam, but its effect is not exactly the same as that of diazepam. This product can inhibit the turnover rate of norepinephrine in the brain and muscle contracture (type 2). Its mechanism of action is mainly to produce sedation and hypnosis by inhibiting the reticular formation activation system on the limbic system of the brain, especially the amygdala. Commonly used benzodiazepines resist convulsions caused by muscle contracture. They are strong against γ-type muscle contracture and weak against α-type muscle contracture. This product has a strong inhibitory effect on both γ-type and α-type muscle contracture, so it has Strong central muscle relaxant effect. This product was developed by Japan’s Yifuku Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and was first launched in Japan on March 17, 1984 by Tabei Mitsubishi Co., Ltd. Its indications for marketing are: ① Anxiety, tension, depression, and neurasthenia in neurological disorders and depression Symptoms, as well as anxiety, tension, and depression caused by physical and mental diseases (hypertension, gastric and duodenal ulcers); ② Anxiety, tension, depression, and muscle tension caused by cervical spine diseases, low back pain, and muscle contraction headaches; ③ Nervous diseases, depression , schizophrenia, psychosomatic diseases (hypertension, gastroduodenal ulcer) and sleep disorders. Etizolam intermediates are mainly used in the preparation of etizolam. This product can be rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration, and is finally excreted from the body through feces and urine. After hepatic metabolism, the plasma t1/2 of the original drug is about 3 hours, and the t1/2 of the metabolite is 8 to 16 hours. Long-term use has no accumulation effect. Less acute toxicity. Drug dependence is almost identical to existing benzodiazepines.
Preparation[1]
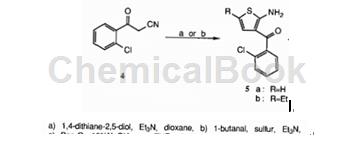
The etizolam intermediate is prepared as follows: o-cyanoethyl chloride is treated with 1,4-dithian-2.5-diol and ‘or 1-butyraldehyde to obtain the etizolam intermediate, with a yield of 57%.
Main reference materials
[1]CN201610413471.4 Stable tablets of etizolam and preparation method
[2]THESYNTHESISOFTHlENOTRlAZOLOTHlAZtPlNES

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

