Overview[1]
Camphor benzalkonium methyl sulfate is in the form of white powder, with a flash point of >100°C and a melting point of 210°C. The purity of commercially available products is >95%. It is insoluble in mineral oil and soluble in water, isopropyl alcohol and glycerin. In sunscreen products, the maximum allowable mass fraction in the EU and China is 6%, but it is not approved for use in the United States and Japan. Stability/Storage: Generally stable; store in airtight containers in a dry and cool environment.
Apply[2]
Camphor benzalkonium methyl sulfate can be used as cationic sunscreen agents. They have high directivity and have both photoprotective and conditioning effects.
In recent years, some literature has discussed changes in the structure and properties of hair exposed to solar radiation. The resulting various types of damage include: fading and swelling of natural or artificial hair color, degradation of tryptophan, transfer of lipids and intercellular colloids, loss of fiber tensile strength, etc. Various physical and chemical methods can be used to evaluate the damage. Evaluation methods include: mechanical property measurement, scanning electron microscopy, optical image analysis, fluorescence and Raman spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy and chromatography, etc.
Some of the chemical reactions that have been identified as responsible for hair shine degradation include: disulfide bond cleavage and thiol formation, oxidation of unsaturated lipids and cholesterol, breakdown of tryptophan, covalently bound lipids [18-methyl Decomposition of eicosanoic acid]. Most of the above changes can be detected in hair exposed to a dose of 50,000 J/cm2 for a long time. It has also been confirmed that when the radiation dose is less than 5000J/cm2 (equivalent to a wavelength range of 250-800nm, the total radiation dose is 415W/m2, and the total radiation dose at a wavelength of 340nm 0.35W/m2 irradiation for 33 h), oxidation of surface lipids (leading to an increase in combing force) and decomposition of tryptophan will also occur.
For more than a decade, there have been patents and scientific literature discussing the photoprotective effects of hair. Suggest methods such as adding sunscreen to conditioner, using antioxidants, or free radical quenchers. Due to the poor directness of these substances to the hair, they are not adsorbed on the surface of the hair after rinsing, and the results are very unsatisfactory. In recent years, some cosmetic raw material companies have developed cationic sunscreen agents, which are highly direct and have both photoprotective and conditioning effects (Figure 5-2-5).
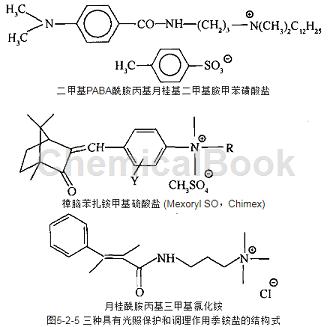
Main reference materials
[1] Modern cosmetic science and technology·Volume 1
[2] Modern Cosmetic Science and Technology·Volume

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

