Background and overview[1]
Alpha-keto acid itself does not contain nitrogen. It can be converted into the corresponding amino acid through transamination or amination in the blood, which helps to reuse urea nitrogen, thus reducing the blood urea nitrogen content. Compound alpha-keto acid tablets (opened in 1996) developed and marketed by Fresenius Kabi, Germany, are used to treat chronic renal failure (CRF) and diseases caused by protein metabolism disorders caused by renal insufficiency. It can alleviate renal function damage and delay the start of dialysis. The chemical name of α-ketophenylpropionic acid calcium salt is 2-oxo-3-phenyl-calcium propionate, which is one of the main components of compound α-ketoacid tablets. The main synthesis methods of α-ketophenylalanine include: hydantoin and benzaldehyde synthesis method, namely the hydantoin method, α-acetamidocinnamic acid hydrolysis method and double carbonylation method. Its calcium salt can be directly produced through the action of a catalyst. Pick. Although the dicarbonylation method has a simple operation method and high product purity, it requires the use of high-pressure reaction equipment and expensive metal catalysts. Therefore, compared with the first two synthesis routes, the process conditions and costs are relatively high. When forming calcium salts, since α-ketophenylalanine has poor thermal stability and is easily oxidized in air, the literature uses a double carbonylation method to directly synthesize α-ketophenylalanine calcium salt under high temperature, high pressure and metal catalyst conditions. , without double carbonylation. There are few literature reports on the use of other methods to synthesize α-ketophenylpropionic acid calcium salt under normal pressure and metal catalyst-free conditions, and the last step of calcium salt formation has only been reported about low alkyl substituted keto acids such as propyl and butyl. Report on salt synthesis.
Preparation[1]
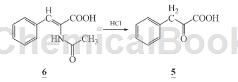
1) Preparation of α-ketophenylalanine calcium salt (1): Dissolve 60 g (0.37 mol) α-ketophenylalanine (5) in 273 mL methanol, lower the temperature below 15°C, and stir Add 57.7 mL triethylamine dropwise for 30 minutes. Stir for 30 minutes. Add 273 mL of calcium chloride methanol solution dropwise below 15°C. Complete the dropwise addition for 2 hours. A solid will precipitate. After stirring for 2 hours, cool and crystallize. After suction filtration, the filter cake was rinsed with 30 mL of methanol and filtered to dryness to obtain 52.3 g of light yellow powdery solid calcium salt of α-ketophenypropionate (1) crude product with a yield of 78.0%. The crude product was recrystallized with water to obtain 41.7 g. White powder, recrystallization yield 79.8%. Atomic absorption spectrum: Ca 10.83% (theoretical value: 10.92%).
2) Add 1600 mL (1 mol/L) hydrochloric acid to the reaction bottle, add nitrogen, add 100g (0.487 mol) α-acetylaminocinnamic acid (6) under stirring, complete the addition, raise the temperature to reflux, react 3 h, filter while hot to remove oily impurities, and the filtrate will crystallize after cooling. Precipitate α-ketophenylalanine (5), filter with suction, and dry the filter cake naturally to obtain 65.3 g of light yellow needle crystal solid ketone α-phenylalanine (5), with a yield of 81.6% (document conversion rate 50 %), m.p.157~158℃ (literature value m.p.157℃).
Content determination[2]
At present, the synthesis process of calcium ketophenylalanate is generally made by the reaction of hydantoin and benzaldehyde. In the current domestic standards, ion exchange chromatography is used to check the relevant substances of calcium ketophenylalanine API, but Only the impurity content is controlled, and the structure of the related substance (i.e. the impurity) is not determined (State Food and Drug Administration standard YBH01512010, related substances part). Moreover, existing detection and analysis methods (such as ion exchange chromatography) all use the main component self-control method. This method is suitable for when the reference substance cannot be obtained and the impurity and the main component absorb corresponding factors close to each other at the same wavelength. Accurate quantification. Existing chromatographic analysis ignores the problem of the corresponding factors of impurity components. The main component self-control method without adding correction factors has certain limitations and cannot accurately quantitatively measure impurities. Therefore, it is impossible to scientifically measure impurities. Calcium ketophenylalanate API was used for quality control.
The method for detecting the phenylacetic acid impurity content in calcium ketophenylalanine. The specific steps are: accurately weigh an appropriate amount of calcium ketophenylalanine raw material, add water to dissolve it with ultrasound, and dilute it with water to obtain calcium ketophenylalanine with a concentration of 1 mg·mL-1 test solution; accurately weigh an appropriate amount of phenylacetic acid reference substance, add water to dissolve it with ultrasound, and dilute with water to a reference solution with a phenylacetic acid concentration of 20 μg·mL-1; test the test solution according to the following chromatographic conditions Carry out analysis and calculate the phenylacetic acid content based on the peak area according to the external standard method. The chromatographic conditions are: (1) Chromatographic column: octadecylsilane bonded silica gel column (2) Mobile phase: 20mmol·L-1 potassium dihydrogen phosphate (phosphoric acid adjusted to pH 3.3)-acetonitrile (85:15, v/ v) is isocratic elution of the mobile phase; (3) Flow rate: 1mL·min-1; (4) Detection wavelength: 205nm; (5) Column temperature: 30°C; (6) Injection volume: 10uL. For the external standard method, see the textbook (“Instrumental Analysis”, Higher Education Press, Fourth Edition). The chromatographic column described therein is an octadecylsilane bonded silica gel column, and the preferred model is an Agilent XDB C18 chromatographic column; the content of the phenylacetic acid described therein in the calcium ketophenylalanine raw material drug shall not exceed 0.2%. Among them, the preparation method of the phenylacetic acid reference substance is: (1) Preparation method: Take the calcium ketophenylalanine raw material, add 0.5% H2O2, leave it at room temperature for 2 hours, add an appropriate amount of water, dissolve it with ultrasound, and use the preparation solution The impurity (phenylacetic acid) was prepared by phase chromatography. Collect the eluates containing the target substance for 30-35 minutes, combine them, concentrate under reduced pressure at 60°C to a certain amount, freeze-dry for 3 days, and further remove ammonium formate to obtain a white flake solid, which is recrystallized to obtain phenylacetic acid reference substance; (2) Preparing colorsThe conditions are: use YMC-Pack ODS-A chromatographic column, use 10 mmol·L-1 ammonium formate solution (formic acid adjusts pH to 4.0) – acetonitrile (85:15, V/V) as the mobile phase for isocratic elution, flow rate The value is 10mL·min-1, the detection wavelength is 205nm, the column temperature is 30°C, and the injection volume is 2mL. The HPLC purity of the phenylacetic acid is higher than 98.5%. The described method for determining phenylacetic acid in the calcium ketophenylalanate raw material drug is to prove that it is accurate, reliable and reproducible.
Main reference materials
[1] Synthesis of α-ketophenylpropionic acid calcium salt
[2] CN201410557834.2 Method for detecting impurity content in calcium ketophenylalanine

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

