Background and overview[1]
Phenylhydrazine is a white monoclinic prism crystal or oily liquid, slightly soluble in water, with a melting point of 19.5°C and a boiling point of 243.5°C. It has an aromatic smell and gradually oxidizes to yellow in the air. Phenylhydrazine is used in the production of pesticides to synthesize 1-phenyl semicarbazide, the intermediate of the organophosphorus pesticide triazophos, and 1-phenyl-3,6-dihydroxypyridazine, the intermediate of pyridazinathion. It is also a bactericidal agent. It is an intermediate for the new varieties of oxathiazolin and imidazolin. In addition, phenylhydrazine, as an organic synthetic raw material, is also used as an intermediate in dyes, pharmaceuticals and other industries, and as an analytical reagent. It can react with the aldehyde and ketone groups of sugars to generate stable glycosides, and the crystal form and melting point of glycosides can be used to identify different reducing sugars.
Preparation[1]
The preparation method of phenylhydrazine is usually by using aniline as raw material and going through diazotization, reduction, acid precipitation, neutralization and other processes. Through the diazotization reaction of aniline and sodium nitrite in an acidic medium, a diazonium salt is formed, which is then reduced with a reducing agent to form a diazobenzenesulfonate. and prepared. The reducing agents reported in the literature mainly include sodium bisulfite, ammonium bisulfite, sodium sulfite, zinc powder, stannous chloride, etc. The most commonly used reducing agent in industry is a mixture of sodium sulfite and sodium bisulfite. The reduction method of zinc powder and stannous chloride is mainly used for laboratory preparation. Phenylhydrazine is synthesized through diazotization reaction. The intermediate diazonium salt is unstable and easy to decompose. It needs to be carried out at low temperature. The reaction steps are many, the production process is complex, and the energy consumption is high. The total yield is only about 80%; during the reaction process, side effects There are many products and wastes, and a large amount of organic salty wastewater will be produced. Environmental treatment is difficult and costly, and it can easily cause environmental pollution. CN201810056083.4 provides a new method for preparing phenylhydrazine with simple process, high yield, low energy consumption, less waste, low production cost, and green and environmental protection.

Place 188g of phenol, 166.7g of 90% hydrazine hydrate and 37.6g of D81 macroporous resin in a four-necked flask with stirring, thermometer and distillation column, start stirring, and heat to 110℃~120℃ , extract water vapor at a temperature of 98°C to 100°C at the top of the distillation column, react for 6 to 8 hours, end the reaction when no condensed water flows out from the top of the distillation column, and then recover excess hydrazine hydrate by distillation under reduced pressure. After the recovery of hydrazine hydrate is completed Use a centrifugal filtration device to separate the D81 macroporous resin, and wash the remaining liquid with an appropriate amount of sodium carbonate solution and pure water to obtain 200.6g of phenylhydrazine.
Wastewater treatment[2]
CN02138294.8 provides a method for the treatment and resource recovery of phenylhydrazine production wastewater. The method includes the following steps: pretreating two types of wastewater generated during the phenylhydrazine production process at a temperature of 0~50°C and Under flow conditions of 1~6BV/h, through an adsorption column filled with macroporous adsorption resin with a polystyrene structure, the effluent is adsorbed and then biochemically treated; the macroporous adsorption resin that has adsorbed organic matter such as phenylhydrazine is used as a desorbent. Desorption regeneration. After treatment by the present invention, the CODcr of the wastewater is reduced from about 28000mg/l to 700mg/l. After biochemical treatment, it can reach the standard discharge; about 6.2 kilograms of phenylhydrazine hydrochloride can be recovered from each ton of waste; by-products generated during the treatment process. The calcium sulfate produced can be used as a cement additive and a filler in building materials products, thereby achieving resource recovery and comprehensive utilization while treating wastewater.
Feeding device[3]
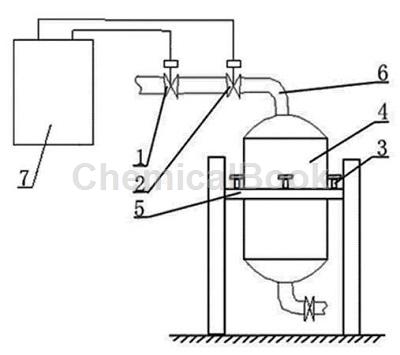
The phenylhydrazine metering tank controls the feeding device, which includes a feeding control valve 1, a shut-off valve 2, a pressure sensor 3 and a phenylhydrazine metering tank 4. The phenylhydrazine metering tank 4 is installed on the bracket 5 in the middle. The phenylhydrazine metering tank There are pressure sensors 3 installed in four directions around 4. The lower end of the pressure sensor 3 is installed on the bracket 5. The cut-off valve 2 is installed on the feed pipe 6 at the upper end of the phenylhydrazine metering tank 4. The feeding control valve 1 is installed on the outer end of the cut-off valve 2. On the pipeline; the phenylhydrazine metering tank control feeding device is connected to the signal line of the electrical control box 7; the phenylhydrazine metering tank control feeding device is controlled and operated by the electrical control box 7.
The pressure sensor 3 is installed between the phenylhydrazine metering tank 4 and the bracket 5. The phenylhydrazine metering tank 4 is supported in the air by the pressure sensor 3.
When used, the pressure sensor transmits the weight of the liquid in the phenylhydrazine metering tank to the relay inside the electrical control box through the signal source or signal line. Once the weight in the phenylhydrazine metering tank reaches the minimum requirement, the phenylhydrazine raw material needs to be replenished. The relay acts and transmits the signal to the feeding control valve and cut-off valve through the signal line. The cut-off valve opens instantly, the feeding control valve opens slowly, and the phenylhydrazine raw material starts to be supplied. The liquid weight in the phenylhydrazine metering tank is sensed by the sensor and reaches the highest setting. request, the relay acts again, and controls the cut-off valve and feeding control valve through the signal line again. The cut-off valve will close instantly, and the feeding control valve will close slowly. The two valves are dual-controlled, safe and reliable. One of the two valves is fast and the other is slow. Not only can the amount of supply be accurately controlled, but it can also be dual-controlled by two valves. Even if one valve has a problem, the other one can take control in a short time. The design of this device does not require manual opening of the manhole to continuously measure the phenylhydrazine metering tank. Liquid level observation and manual replenishment are time-consuming and labor-intensive, and phenylhydrazine is toxic. Direct observation without manual observation also plays a role in personal safety protection. Using this device is convenient, fast, safe and reliable, and has high work efficiency.�There will also be no shortage of supplies or oversupplies due to human factors.
Main reference materials
[1] [Chinese invention] CN201810056083.4 A preparation method of phenylhydrazine
[2] CN02138294.8 Treatment and resource recovery method of wastewater from phenylhydrazine production
[3] [China Utility Model] CN201420179689.4 Phenylhydrazine metering tank control feeding device

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

