Basic background and overview[1][2]
P-isopropylaniline is a colorless liquid, soluble in benzene and other organic solvents. Para-isopropylaniline is an alkyl-substituted aniline-like compound, also known as cumamine. It is mainly used in the synthesis of the chemical herbicide isopropuron, pesticide additives, medicines, materials (paints, dyes) and other pesticide chemicals. It is also used For the analysis of tungsten.
In terms of industrial production, foreign countries such as the United States and Japan have successfully researched and developed the industrial production technology of isopropylaniline as early as the 1980s and used it to develop many series of products with special functions. At present, domestic para-isopropylaniline is mainly imported from abroad, and there are not many reports on its production. With the increasing demand for para-isopropylaniline in the international and domestic markets and the continuous expansion of the use of this product, there is broad prospect for developing a synthesis process for para-isopropylaniline.
Synthesis method[1][2][3][4][5]
Synthetic route 1: Iron powder reduction method
Using cumene as the starting material, it is homogeneously nitrated in concentrated sulfuric acid medium to obtain a nitrocumene mixture. The reaction mixture is reduced and separated by iron powder to obtain p-isopropylaniline with a content of ≥97%. The nitration yield of this reaction was 72.4%, the reduction yield was 92.3%, the separation yield was 93.6%, and the total yield was 62.6%.

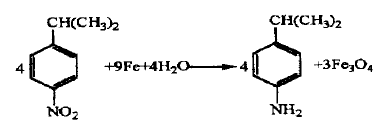
Synthetic route 2: Hydrogenation reduction method
Using cumene as the starting material, after nitration with mixed acid, catalytic hydrogenation is carried out under normal pressure. The hydrogenation reaction uses Cu/SiO2 as the catalyst, the reaction temperature is 290~310℃, the contact time is 0.31~0.34 s, the nitro compound space velocity is 0.23h-1, and the selectivity to isopropylaniline is 95 About %, the nitro conversion rate reaches over 99%.
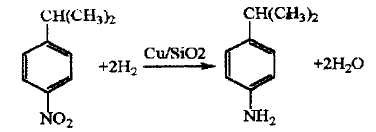
Application fields[6][7][8]
1. Synthetic herbicide isoproturon
Isoproturon is a replacement urea herbicide with a broad spectrum of herbicides. It is mainly used in wheat, barley,In crop fields such as cotton, peanuts, corn, soybeans, peas, broad beans, etc., it has little toxicity to mammals and has obvious production-increasing effects. Para-isopropylaniline is the main raw material for the synthesis of isopropuron. Currently, the production of isopropylaniline at home and abroad is carried out according to the phosgene route. The synthesis method is as follows.
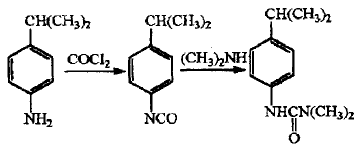
2. Preparation of indole and its derivatives
Using p-isopropylaniline as raw material, diazotization, cyclization reaction with ethyl-2-methyl-acetoethyl ester and KOH to obtain II, which was dissolved in ethanol, degreased with KOH, and acidified with crude acid to obtain III. Add III to a high boiling point solvent and deacidify it with cuprous salt to obtain 5-isopropyl indole (I). Compared with the existing inventions, this method obtains a new indole derivative, 5-isopropyl indole, which plays an important role in the construction of drugs and biological activities. It is comparable to the current preparation of alkyl-substituted indole derivatives. ratio, the synthesis route is cutting-edge, the raw materials are cheap, and the yield is high, up to 60%~70%.
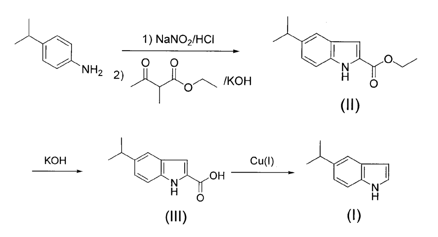
3. Preparation of amide compounds
Amide compounds are a very important class of chemical substances that are widely used in pesticides, polymers, materials, biologically active substances and other fields. Traditionally, amide compounds are synthesized mainly through amines and chemically active carboxylic acid salts of organisms and alcohols. , aldehydes and other coupling reactions, or prepared through the amine exchange reaction between chemically active primary amides and fatty amines. A patent points out that palladium salts and ligands can be used as catalysts to mix N,N-dimethylformamide compounds, aniline compounds, protonic acids, Lewis acids and organic solvents, and heat them to prepare amide compounds. For example, use p-isopropylaniline and N,N-dimethylformamide as raw materials, add appropriate catalysts and solvents, and prepare N-(4-isopropylphenyl)formamide.

Degradation characteristics[9]
P-isopropylaniline is an aniline substitute and is easily discharged into the environment along with industrial wastewater, agricultural runoff water, and domestic sewage, causing potential harm to aquatic organisms and human health, and posing certain environmental risks. Para-isopropylaniline in sewage mainly comes from the synthesis and metabolism of the herbicide isopropuron. Aerobic biochemical wastewater treatment simulation experiments show that when the HRT is 6h, 12h, and 24h, the removal rates of p-isopropylaniline are 66%, 76%, and 91% respectively, and the degradation half-life in aerobic activated sludge is 16.16h.
Main reference materials
[1] Zhang Pengfei, Yang Liancheng, Wang Jiushan. Synthesis and application of isopropylaniline [J]. Tianjin Chemical Industry, 2003, 17(3): 28-30.
[2] Wang Lianggui, Luo Hean, Duan Zhengkang. Synthesis of isopropylaniline [J]. Chemistry World, 1997.11:581-583.
[3] Fediriva P I et al. Amination of Aromatic Compounds by Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride[J].Zh Prikl klim. 1973, 46(5):1079- 1082.
[4] Baardman Frank, et al. Process for the Selective Alkylation of an Aniline[P]. EP 79 093,1982.
[5] Takuji N. Preparation of 4- Isopropylanilne[ P].JP 4069 366,1992.
[6] Zhang Sigui. Handbook of Practical Fine Chemicals, Organic Volume (Part 2) [M]. Beijing Chemical Industry Press, 1996.1553.
[7] Feng Li, Heng Zhang Liwei, Wang Xiaoju, 5-alkyl substituted indole derivatives and their preparation method, CN 200810055352, application date 2008-07-04
[8] Guo Xunxiang, Gu Dawei, a method for preparing N-aryl amide compounds, CN 201510259837, application date 2015-05-20
[9] Gu Wen, Zhou Linjun, Liu Jining, et al. Degradation characteristics of three aniline chemicals in aerobic wastewater treatment simulation system [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 1: 036.
Running water and domestic sewage are discharged into the environment, causing potential harm to aquatic life and human health, and posing certain environmental risks. Para-isopropylaniline in sewage mainly comes from the synthesis and metabolism of the herbicide isopropuron. Aerobic biochemical wastewater treatment simulation experiments show that when the HRT is 6h, 12h, and 24h, the removal rates of p-isopropylaniline are 66%, 76%, and 91% respectively, and the degradation half-life in aerobic activated sludge is 16.16h.
Main reference materials
[1] Zhang Pengfei, Yang Liancheng, Wang Jiushan. Synthesis and application of isopropylaniline [J]. Tianjin Chemical Industry, 2003, 17(3): 28-30.
[2] Wang Lianggui, Luo Hean, Duan Zhengkang. Synthesis of isopropylaniline [J]. Chemistry World, 1997.11:581-583.
[3] Fediriva P I et al. Amination of Aromatic Compounds by Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride[J].Zh Prikl klim. 1973, 46(5):1079- 1082.
[4] Baardman Frank, et al. Process for the Selective Alkylation of an Aniline[P]. EP 79 093,1982.
[5] Takuji N. Preparation of 4- Isopropylanilne[ P].JP 4069 366,1992.
[6] Zhang Sigui. Handbook of Practical Fine Chemicals, Organic Volume (Part 2) [M]. Beijing Chemical Industry Press, 1996.1553.
[7] Feng Li, Heng Zhang Liwei, Wang Xiaoju, 5-alkyl substituted indole derivatives and their preparation method, CN 200810055352, application date 2008-07-04
[8] Guo Xunxiang, Gu Dawei, a method for preparing N-aryl amide compounds, CN 201510259837, application date 2015-05-20
[9] Gu Wen, Zhou Linjun, Liu Jining, et al. Degradation characteristics of three aniline chemicals in aerobic wastewater treatment simulation system [J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 1: 036.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

