Background and overview[1][2]
The Chinese alias of 5-amino-2-chlorobenzoic acid is 2-chloro-5-aminobenzoic acid, CAS number 89-54-3, chemical formula C7H6ClNO2. Molecular weight 171.58100. White – similar to crystalline powder, density 1.5, melting point 184-188 °C (lit.), boiling point 373.3ºC at 760 mmHg, flash point 179.6ºC, refractive index 1.648. 5-Amino-2-chlorobenzoic acid can be used in pharmaceutical and chemical industries Synthetic intermediates.
If 2-bromomethyl-4-fluorobenzoic acid methyl ester is inhaled, move the patient to fresh air; if skin contact occurs, remove contaminated clothing and wash the skin thoroughly with soap and water, if any If you feel unwell, seek medical attention; if eye contact occurs, separate eyelids, rinse with running water or saline, and seek medical attention immediately; if ingested, rinse mouth immediately, do not induce vomiting, and seek medical attention immediately.
Apply[1][2]
5-Amino-2-chlorobenzoic acid can be used as a pharmaceutical and chemical synthesis intermediate. Examples of its application are as follows:
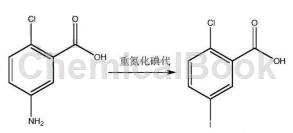
1. Preparation of 2-chloro-5-iodobenzoic acid.
2-Chloro-5-iodobenzoic acid is the starting material for the synthesis of SGLT-2 inhibitors such as dapagliflozin and empagliflozin. The existing production methods are complex and costly. The new synthesis method uses methyl anthranilate as the starting material, and obtains the product through steps such as iodination, transesterification, diazotization and chlorination, and hydrolysis.
Some studies have added 2-chloro-5-aminobenzoic acid to the solvent sulfuric acid aqueous solution, added sodium nitrite aqueous solution dropwise at -10°C to 10°C, and stirred until there is no solid in the reaction solution; after the reaction is completed, urea is added to remove unreacted sodium nitrite, then add potassium iodide aqueous solution at a temperature of -10°C to 10°C, stir at room temperature until the reaction is complete, filter, and dissolve the filter cake with ethyl acetate, wash, dry, and concentrate under reduced pressure to dryness to obtain a crude product, and then Refined with toluene or isopropyl alcohol to obtain 2-chloro-5-iodobenzoic acid.
2. Preparation of fluopyrimifen.
Butafenacil (English common name butafenacil, trade name Inspire) is a non-selective uracil herbicide developed by Syngenta. It was launched in 2001 and is mainly used to control gramineous weeds, broadleaf weeds and sedges in vineyards, cotton and non-cultivated land. The pre-emergence and post-emergence weeding dosages are both 75-150 g/hm2. The synthesis reaction formula is as follows:

The specific steps are as follows:
Step 1: Synthesis of intermediate M-1
Into the 250 mL reaction bottle, add 10.08 g (50.00 mmol) of 5-amino-2-chlorobenzoic acid and 70 mL of toluene in sequence, stir at room temperature for 5 minutes, and then add 23.79 g (200 mmol) of thionyl chloride dropwise. , after the dropwise addition is completed, heat and reflux until no hydrogen chloride gas is released. Evaporate toluene and excess thionyl chloride under reduced pressure, cool down to obtain a yellow oil, add 50 mL anhydrous tetrahydrofuran, stir to dissolve, and seal.
Step 2: Synthesis of intermediate M-2
Add 120 mL anhydrous tetrahydrofuran to the 500 mL reaction flask under an ice-water bath, cool down for 30 min, add 2.00 g (50 mmol) of 60% sodium hydride in batches, stir for 10 min, and then add 2-hydroxyisobutyl dropwise. Allyl acid ester 5.77 g (40.00 mmol), the dropwise addition is completed.�, stirred at room temperature for 4 h and then stopped the reaction.
Step 3: Synthesis of intermediate M-3
Add the above M-1 tetrahydrofuran solution drop by drop to the M-2 solution. The reaction system gradually changes from white to yellow. After the dropwise addition is completed, stir at room temperature for 2 hours. TLC shows that there is no remaining raw material in the reaction. Pour the mixture into 100 mL ethanol, stir for 30 min, and evaporate the solvent under reduced pressure. Add 100 mL water to the residue, extract with ethyl acetate (100 mL×2), and combine the organic phases. The organic phase was washed with water, washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, desolvated under reduced pressure, and purified by column chromatography to obtain 2.52 g of yellow oil M-3, with a mass fraction of 86% and a yield of 18% (using 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid Allyl ester meter). The yellow oil was used directly in the next reaction.
Step 4: Synthesis of intermediate M-4
Add 9.16 g (50.00 mmol) of 3-amino-4,4,4-trifluorocrotonate ethyl ester and 150 mL of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran into a 500 mL reaction bottle, and add sodium hydride in batches to the above solution under an ice-water bath. 6.00 g (150 mmol). After the incubation reaction for 1 hour, add N,N-dimethylcarbamoyl chloride dropwise. After the addition is completed, heat and reflux for 1 hour. TLC shows that there is no raw material remaining. The mixture was then slowly poured into ethanol, stirred at room temperature for 10 min, and desolvated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by column chromatography to obtain 6.2 g of red oil M-4, with a crude yield of 49%, which was directly used in the next step of the reaction.
Step 5: Synthesis of intermediate M-5
Add 1.49 g (5.00 mmol) M-3, 1.90 g (7.50 mmol) M-4 and 30 mL glacial acetic acid into the 100 mL reaction bottle. After heating and refluxing for 4 h, TLC showed that the reaction was complete. After the acetic acid was evaporated under reduced pressure, the residue was poured into 20 mL of water, then ethyl acetate (30 mL × 2) was added for extraction, and the organic phases were combined. The organic phase was washed with water and saturated brine, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and desolvated under reduced pressure. Purified by column chromatography, 1.21 g of white solid was obtained, with a mass fraction of 98.5%, a yield of 51.7%, and a melting point of 176-178°C.
Step 6: Synthesis of fluopyrimifen
Add 1.21 g (2.63 mmol) M-5 and 20 mL DMF into the 100 mL reaction flask, stir at room temperature for 5 min, then add 0.44 g (3.15 mmol) of potassium carbonate, continue stirring at room temperature for 10 min, and then add 0.50 g of methyl iodide. (3.15 mmol). After stirring at room temperature for 2 h, TLC showed that the reaction was complete. Pour the mixture into 40 mL of water, add ethyl acetate (30 mL×2) for extraction, and combine the organic phases. The organic phase was washed with water, washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, removed under reduced pressure, and purified by column chromatography to obtain 0.62g of crude product. Recrystallize with ethyl acetate and petroleum ether to obtain 0.54 g of white solid, with a mass fraction of 99.2%, a yield of 43%, and a melting point of 111~112°C.
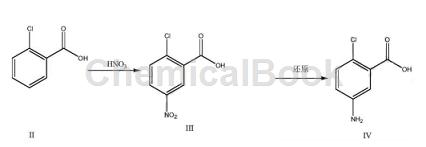
Preparation[1]
1) Put the solvent concentrated sulfuric acid and o-chlorobenzoic acid into the reaction vessel, control the temperature to -5~5℃, add nitric acid dropwise, and keep the reaction for 1~3h after the dripping. After the reaction is completed, quench with ice water, and then stir, Centrifuge, wash with water and dry to obtain 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid;
2) Add ethanol-water mixed solvent, 2-chloro-5-nitrobenzoic acid, iron powder and ammonium chloride into the reaction vessel, heat and reflux for 3 to 8 hours; filter while hot after the reaction is completed, and the filtrate Concentrate to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product, which is then refined by adding ethyl acetate or toluene to obtain 2-chloro-5-aminobenzoic acid.
Main reference materials
[1] CN201611010716.5 A preparation method of 2-chloro-5-iodobenzoic acid
[2] Guo Zhengfeng, Chen Lin, Ying Junwu, et al. Synthesis and biological activity of fluopyrimifen [J]. Modern Pesticides, 2017, 16(5): 13-16.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

