Background and overview[1][2]
Benzoin, also known as benzoin, is an important semi-synthetic intermediate and photopolymerization catalyst. The classic preparation method is to obtain it from the condensation reaction of two molecules of benzaldehyde under the catalysis of sodium cyanide (potassium). Although the yield is high, it is highly toxic, which not only damages the environment but also affects health. Thiamine hydrochloride (vitamin B1) is a compound containing a thiazole ring and can be used to catalyze this reaction instead of cyanide. Research on the oxidation reaction of benzoin has a long history. Its oxidation product is mainly benzoyl, namely diphenylethylenedione, which is an important organic chemical raw material and an intermediate for synthetic drugs. It is widely used in medicine, spices and daily necessities. It has a wide range of applications in chemical production. Classic benzoin synthesis uses sodium cyanide or potassium cyanide as a catalyst, which promotes the condensation of two molecules of benzaldehyde under the action of cyanide anions (CNˉ). Although the yield is high, it is highly toxic, damaging the environment and affecting health. The traditional method uses benzaldehyde as the raw material, catalyzes the reaction under alkaline conditions for 1.5 hours, uses cyanide as the catalyst, and obtains the benzoin product through the condensation reaction. Due to the high toxicity of the catalyst, the experiment is dangerous, and this method has been abolished in recent years. Inspired by the condensation mechanism of CNˉ benzoin, chemists discovered in the late 1970s that vitamin B1 could replace CNˉ as the catalyst for benzoin condensation without using highly toxic NaCNˉ or KCNˉ. Many chemists at home and abroad are exploring new synthesis conditions to replace the disadvantages of water-soluble methods. The ultrasonic cavitation phase transfer catalytic method is a new type of synthesis method. This method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions and less pollution. It can also speed up the material transfer between the liquid and liquid phases. Ultrasonic cavitation produces tiny bubbles, which can reduce phase transfer. The amount of catalyst used can even eliminate the need for a phase transfer catalyst, which has significant advantages such as significantly increasing the yield.
Apply[1-3]
Benzophenone is an important semi-synthetic intermediate and photopolymerization catalyst. Examples of its application are as follows:
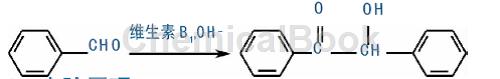
1. Benzoin oxidation reaction. The most mature synthesis of benzoyl is from the oxidation of benzoin. It is the most commonly used synthetic route for benzil. There are many oxidants used to oxidize benzoin to synthesize benzoyl, most of which are weak oxidants. However, the oxidation methods can be divided into two types. One is the direct oxidation method, using inorganic compounds, organic compounds, metal organic compounds and polymeric compounds as oxidants; the other is the direct oxidation method; One is the indirect oxidation method, which uses a catalyst and microwave radiation for catalysis. The oxidation reaction equation is shown in the figure:

2. Benzoin condensation reaction. Benzoin condensation or benzoin reaction is a method for the synthesis of 1,2-diphenylhydroxyethanone. It is widely used in chemical industry and drug synthesis. For example, this reaction is used in the synthesis of the anti-epileptic drug diphenylhydantoin and the preparation of diphenylethylenedione, diphenylethylenedione oxime, benzoin acetate, etc. Therefore, in-depth study of the condensation reaction of benzoin has theoretical and practical significance for improving yields and expanding applications. The classic synthesis of benzoin uses sodium cyanide or potassium cyanide as a catalyst. Although the yield is high, it is highly toxic, damaging the environment and affecting health. The coenzyme synthesis catalyzed by vitamin B1 solves this problem and has good development prospects.
Preparation [3-5]
Method 1: Under ultrasonic conditions, a trace amount of quaternary ammonium salt dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium bromide is used as a phase transfer catalyst and vitamin B1 is used as a catalyst to synthesize benzoyl ketone through the aldol condensation of benzaldehyde. This method has the advantages of simple operation, mild reaction conditions, high yield and good reproducibility. The specific steps are: add dodecyldimethylbenzylammonium bromide (0.02 g), distilled water (3 mL), ethanol (95%, 7.5 mL), and vitamin B1 (0.9) into a dry 100 mL three-necked bottle. g), plug the bottle mouth, shake well to dissolve completely. Place in an ice-salt bath to fully cool and maintain at -5°C. Place a NaOH solution of a certain concentration in an ice-salt bath to fully cool down and keep it at -5°C. Add this NaOH solution to a three-necked flask, then add freshly steamed benzaldehyde (5 mL), shake well, and adjust pH = 8.3 ~ 9.3. Based on the color of the reaction solution, you can judge whether the amount of alkali is appropriate. Install the reflux tube and place it in an ultrasonic cleaner water bath (65°C) for 30 minutes. The solution in the three-necked bottle will completely penetrate into the water bath to maintain the pH value.

Method 2: Use ultrasonic cavitation and phase transfer catalysis, use water/ethanol as the reaction medium, benzaldehyde as the raw material, thiamine hydrochloride (VB1) as the catalyst, and react in an alkaline solution to prepare benzoin. The effects of various reaction conditions such as raw material ratio, reaction temperature, reaction time, system pH value, and type of phase transfer catalyst were studied in detail. The optimal conditions obtained from the experiment are: in the ethanol/water binary mixed solution, 5 mL of benzaldehyde, 2.0 g of thiamine hydrochloride, the amount of phase transfer catalyst accounts for 10% to 12% of the mass of benzaldehyde, the amount of distilled water is 2 mL, ethanol The volume was 8 mL, the pH value of the system was controlled between 9.3 and 9.7, the water bath ultrasonic cavitation temperature was controlled at around 70 °C, the reaction time was 90 min, and the ultrasonic power was 80%. Under optimal conditions, the yield reaches 93.57%, and the product content is above 90%. This process has the advantages of mild reaction conditions and high conversion rate. The specific reaction process is: weigh an appropriate amount of VB1 and place it in ice water.In a small, transparent three-necked flask, add 2 mL of water and 8 mL of ethanol, saturate the sodium hydroxide solution (1 mol/L) with cold water, and adjust the pH value to 9.3~9.7. Since VB1 is stable under acidic conditions, it easily absorbs water. , VB1 solution and sodium hydroxide solution must be cooled with cold water before reaction. It is difficult to adjust the pH value in the experiment, and it requires patient dripping of sodium hydroxide solution for a long time. Add an appropriate amount of phase transfer catalyst and 5 mL of freshly steamed benzaldehyde, place it in an ultrasonic cleaner, set the water bath temperature, ultrasonic power, and ultrasonic time, and use a programmed temperature rise method to make the water bath reach the preset temperature and start ultrasonic cleaning. During the reaction, products precipitate from the reaction solution. After the reaction is completed, pour the reaction solution into a small beaker, cool it in an ice water bath and let it stand. After a few hours, it is filtered, washed, and naturally air-dried to obtain the product benzoin. Weigh, calculate the crude yield, and recrystallize with boiling ethanol (the solubility of benzoin in boiling 95% ethanol is 12 to 14 /100 mL). Use a digital melting point meter to measure the melting point and calculate the product purity.
Method 3: A method for preparing benzoin, including the following steps: S1. Mix benzaldehyde, distilled water, and catalyst and shake them thoroughly to prepare a mixed solution. The molar ratio of benzaldehyde, distilled water, and catalyst is 49:400: 6 to 9, adjust the pH value of the mixed solution to 8 to 10 with an alkali solution, and then place it in an electric heating mantle to heat to 50 to 80°C and perform a reflux reaction. The reflux reaction time is 3 to 7 hours, and every time during the reflux reaction Add an alkali solution once every 30 minutes to maintain the pH value of the mixed solution at 8 to 10. After the reaction is completed, cool it naturally. After the crystals are completely separated, filter under reduced pressure to obtain a crude benzoin product; S2. Use the crude benzoin product with a concentration of Pure benzoin is obtained by recrystallizing from 95% ethanol solution.
Main reference materials
[1] Research progress on benzoin oxidation reaction
[2] Improvement of benzoin condensation reaction
[3] Ultrasonic cavitation synthesis of benzoin
[4] Preparation and characterization of phenylethanol ketone
[5] CN201810289121.0 Preparation method of benzoin

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

